객체의 이전 상태를 저장하고 복원할 수 있는 패턴
문서 편집 프로그램 등에서는 별도로 파일을 저장하지 않아도 스냅샷을 기록하여 이전 상태로 복원하는 기능을 제공
예를 들어 Editor 클래스에 커서 위치, 폰트 등의 정보가 private으로 감춰져 있다면 이 내용을 외부 객체에서 직접 가져올 수 없음
memento 패턴을 사용하면 캡슐화를 유지하면서도 현재 상태 스냅샷을 찍을 수 있음
스냅샷 생성을 상태 정보를 가지고 있는 객체에게 위임. 예를 들면, 외부 객체가 Editor 객체에게 스냅샷을 달라고 요청. Editor 객체는 실제 상태를 들고 있기 때문에 스냅샷을 생성할 수 있음.
상태를 저장해서 넘기면서도 캡슐화를 유지하기 위해 memento라는 특수한 객체를 사용함
memento에 담긴 내용은 memento를 만든 객체에서만 접근할 수 있음. memento를 요청한 쪽은 스냅샷의 메타데이터(시간, 이름 등) 정도만 접근 가능.
중첩 클래스를 지원하는 언어에서는 다음과 같이 구현
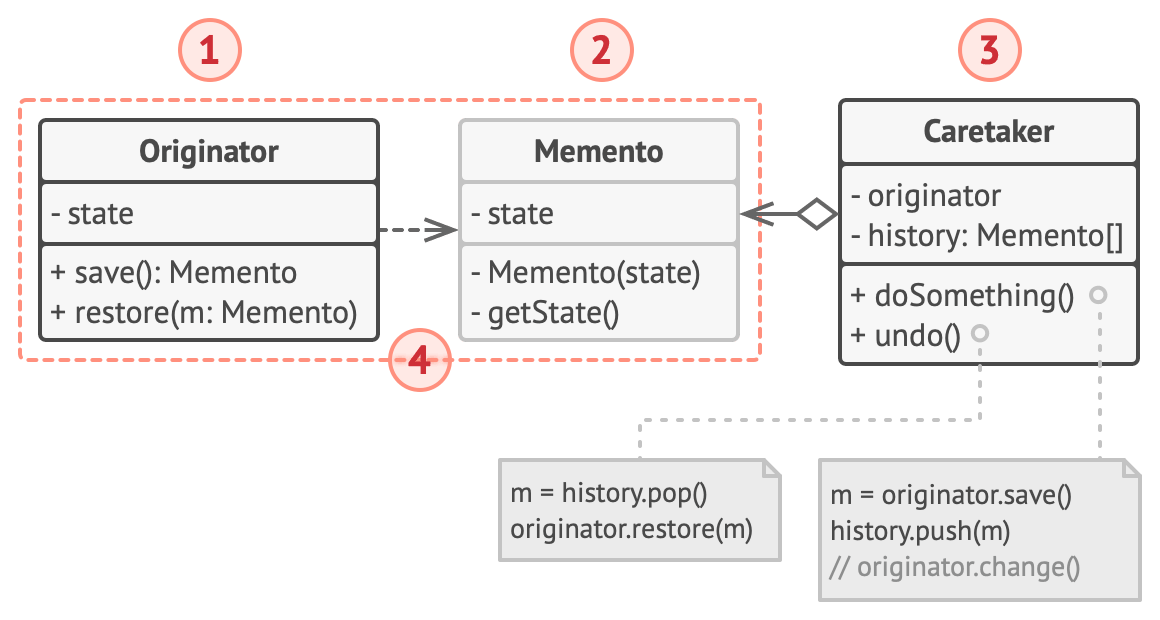
메멘토 패턴은 originator, caretaker, memento 3개의 객체로 구현
- originator: 내부 상태를 실제로 가지고 있는 객체
- 스냅샷(memento 객체)를 생성하거나, 스냅샷으로부터 상태를 복원
- memento: 내부 상태가 저장되어 있는 객체
- caretaker: 실행 취소룰 원하는 객체(클라이언트)
- originator에게 memento 객체를 달라고 요청하여 현재 상태를 저장하고, 가지고 있던 memento 객체를 originator한테 주면서 이 상태로 복구해달라고 요청할 수 있음
- 스냅샷을 찍어야 하는 시기/이유, 복원해야하는 시기/이유 등을 알고 있음(스택 등으로 memento 객체를 관리)
- memento 클래스는 originator 클래스 내부에 중첩되어 있음
- originator는 memento에 대한 모든 접근 권한을 가짐
- caretaker는 memento의 일부 필드(이름, 시간 등 메타데이터)에만 제한적으로 접근 가능
중첩 클래스를 지원하지 않는 언어(php 등)에서는 다음과 같은 구조를 사용
외부 클래스가 memento를 통해 상태에 접근할 가능성을 조금이라도 남기고 싶지 않을 때 다음과 같은 구조를 사용
class Editor {
private var text: String = ""
private var curX: Int = 0
private var curY: Int = 0
private var selectionWidth = 0
fun setText(text: String) {
this.text = text
}
fun setCursor(x: Int, y: Int) {
this.curX = x
this.curY = y
}
fun setSelectionWidth(width: Int) {
this.selectionWidth = width
}
fun createSnapshot(): Snapshot {
return Snapshot(text, curX, curY, selectionWidth)
}
fun restore(snapshot: Snapshot?) {
snapshot?.restore(this)
}
fun printCurrentState() {
println("text: $text\ncursor: $curX, $curY\nselectionWidth: $selectionWidth")
}
inner class Snapshot(
private val text: String,
private val curX: Int,
private val curY: Int,
private val selectionWidth: Int
) {
// internal: 같은 모듈안에서만 공개됨
internal fun restore(editor: Editor) {
editor.setText(text)
editor.setCursor(curX, curY)
editor.setSelectionWidth(selectionWidth)
}
}
}
class Command(private val editor: Editor) {
private var backup: Editor.Snapshot? = null
fun makeBackup() {
backup = editor.createSnapshot()
}
fun undo() {
editor.restore(backup)
// 아래와 같이 사용해도 동일한 결과
// backup?.restore(editor)
}
}val editor = Editor()
val command = Command(editor)
editor.setText("first state")
editor.setCursor(1, 1)
editor.setSelectionWidth(1)
editor.printCurrentState()
/*
text: first state
cursor: 1, 1
selectionWidth: 1
*/
command.makeBackup()
editor.setText("second state")
editor.setCursor(2, 2)
editor.setSelectionWidth(2)
editor.printCurrentState()
/*
text: second state
cursor: 2, 2
selectionWidth: 2
*/
command.undo()
editor.printCurrentState()
/*
text: first state
cursor: 1, 1
selectionWidth: 1
*/- 캡슐화를 유지하고 스냅샷 저장
- 스냅샷 저장/복원은 originator에서, 관리는 caretaker에서 담당하여 코드 분리
- 클라이언트(caretaker)에서 memento 객체를 너무 자주 만들면 메모리를 많이 잡아먹을 수 있음
- caretaker가 memento 객체를 잘 관리해주어야 함(오래된 memento 삭제 등)
- php, python, js 등 대부분의 동적 프로그래밍 언어는 memento 내부 상태가 그대로 유지됨을 보장할 수 없음