Given the root of a binary tree, collect a tree's nodes as if you were doing this:
- Collect all the leaf nodes.
- Remove all the leaf nodes.
- Repeat until the tree is empty.
Example 1:
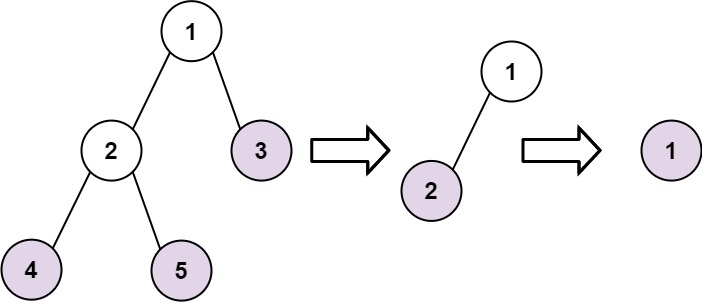
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [[4,5,3],[2],[1]] Explanation: [[3,5,4],[2],[1]] and [[3,4,5],[2],[1]] are also considered correct answers since per each level it does not matter the order on which elements are returned.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [[1]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100