Why Route0x? Query Routing cannot be fully solved just with Text classification or just with Semantic similarity in isolation. Here is why: The query "How can I improve my credit score?" is In-Domain (ID) but Out-of-scope (OOS) for a banking chatbot and Out-Of-Domain (OOD) OOS for a e-Commerce chatbot. A good query router should be able to learn to accept ID In-Scope queries and Reject both ID OOS and OOD OOS. The research literature is vast and it hints Chatbots (or more formally) Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems (TODS) and Goal Oriented Dialogue Systems (GODS) have been grappling with this hard problem for a long time now.
route0x is a production-grade solution that takes a comprehensive approach to query routing, leveraging LLMs while optimizing for cost per query ($/query). 0x your latency, cost and learning curve.
Hitherto, route0x is the
only (practically) free, low latency (no external I/O needed), DIY + Improvable, low shot (only 2 user samples per route/intent needed), production-grade solution, that is FT for only 100 stepsthat matches or beats contemporay Query Routing Researches and Solutions. We tested it on8 different TODS datasets (some are deployed systems) from different domains, granularity and complexityagainst 2 different researches and 1 library. (detailed table below).*
Contributions
- Loss function - Variant of large scale angular margin loss .
- Unsupervised OOS detection - novel combination.
- Uncertainity based fall-back mechanism - via NN.
- Simple trick to do Multi-vector (late interaction) reranking.
Ablations suggest each of these items contribute to the results.
Check out the highlight reel of empirical evals and/or even dig deep with more numbers or get your hands-on with the starter notebook.
- Route0x: Getting Started
- Route0x Evals: A Highlight reel
- I want to know how it works
- I want to understand the knobs and tinker with it
- I want to see more usage samples
- I want to see the detailed numbers & reproduce benchmarks
- Features and Roadmap
- Scope, Caveats and Limitations
- Citations
We've disetangled the resource heavy route building (entails training) from query routing (entails inference)
pip install route0x[build] # (Built with SWEs as target audience)pip install route0x[route] # (Light-weight without any heavy torch dependencies)from route0x.route_finder import RouteFinder
query_router = RouteFinder(<your_route0x_model_path>)
route_obj = query_router.find_route(<your-query>)| Dataset | Domain | Has OOS? | Type | Test Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curekart | E-commerce | Yes | Real-world TODS queries | 991 |
| Powerplay11 | Online Gaming | Yes | Real-world TODS queries | 983 |
| Sofmattress | Furniture | Yes | Real-world TODS queries | 397 |
| CLINC150 OOS - Banking | Banking | Yes | Expert / Synthetic | 1850 |
| CLINC150 OOS - Credit Cards | Credit Cards | Yes | Expert / Synthetic | 1850 |
| Banking 77 | Banking | Yes | Expert / Synthetic | 4076 |
| ACID | Insurance | No | Real-world TODS queries | 11042 |
| ROSTD | Personal Assistant | Yes | Expert written | 11711 |
Goal of this comparison: To show that Route0x beats SetFit + NA and Hosted LLMs in OOS recall while offering best-in class F1 scores across datasets while having miniscule latency needs.
P50 Latency: p50 Latency numbers in the Amazon paper is unclear on couple of levels: 1.) it combines latencies between hosted LLMs and local setfit inferences. For latter case hardware specs are not mentioned 2.) It uses an average across datasets. Our latency numbers based on CPUs ran a Mac M1 Pro 16" machine. While we acknowledge it is not directly comparable (as the hardware specs could be different), but our is assertion if dataset specific route0x p50 latency is lower than a conservative latency estimate of an average across datasets it should be definitely lower than a dataset specific latency. This is shown to just to give a ballpark.
Caveat: Route0x uses SetFit as a base. But not as-is, we added a tweak on how we use it and a few more innovations on top of SetFit. (Jump to "How it works"). But unlike the SetFit + NA option suggested in the paper, We do not perturb positive samples to create hard negatives nor we used any special prompting or CoT for intent/OOS detection. We employ a straight forward Low-shot learning regime that only needs 2-samples from real dataset to simulate real world query routing users (who might find it hard to offer more samples for each route of interest). We augment those 2 samples into to 12 effective samples with LLMs, more on this later. Also we train only for 100 steps. The LLMs used in the paper as for as we can tell are hosted APIs hence by design suffers high latency due to network I/O and incurs $ which makes it infeasible for query routing which might touch many queries even if that is reserved for uncertainity predictions.
Note: All numbers are based on CPU, MPS/CUDA GPU device. Numbers can slightly vary based on the device and seeds. As the paper shows only the best numbers (without any notion of variations denoted usually with ±), we also show the best numbers in this comparison.
Goal of this comparison: To show that Route0x offers robust in-scope accuracy in the presence of adversarial ID OOS and OOD OOS, while having miniscule latency needs.
Caveat: The Route0x base model is all-mpnet-base-v2 but it is compared against purpose-built architectures like TOD-BERT which are architected for and trained on TODS style intent detection and yet we outperform them.
Note: All numbers are based on MPS GPU device. Numbers can slightly vary based on the device and seeds. As the paper shows the all numbers with uncertainity we present numbers from 3 runs and denote the variations with ±.
Goal of this comparison: To show that Route0x beats pure embedding similarity + threshold based approach for query routing, while having miniscule latency needs.
Note: All the above numbers are with use_multivec_reranking = False, (explore below sections for more details)
- BGE-BASE - BAAI/bge-base-en-v1.5,
- MPNET - sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2
Data:For synthetic data generation we leverage both open weight and hosted LLMs. For Open LLMs we integrate ollama and for hosted LLMs we use respective LLM provider libraries.
Training: As the image suggests we have multiple heads to the same model: A setfit model with default logistic regression head, a calibrated head, a LOF and IF head and a faiss index of NNs and a numpy compressed file of multi-vector representation of the NN. Classifier heads will take the first pass, LOF/IF heads help in OOS detection and NNs can help for classifier uncertainity, multi-vector representations help in reranking candidates.
So when run find_route
route_obj = query_router.find_route(query="How can we build an Alarm clock from scratch?")route0x system combines all of its heads returns route_obj
{
'is_oos': True, # LOF / IF head output
'query': 'How can we build an Alarm clock from scratch?',
'route_id': 1,
'route_name': 'NO_NODES_DETECTED', # default label for OOS intents
'prob': 0.56, # Model confidence
'majority_voted_route': 'NO_NODES_DETECTED' # Majority voted NN
'mean_distance_from_majority_route': 1.1501572
}default flow is controlled by return_raw_scores, when False.
route_obj = query_router.find_route(<your_query>, return_raw_scores= False)
if route['is_oos']:
if prob < model_confidence_threshold_for_using_outlier_head:
predicted_route = oos_label
else:
if prob <= model_uncertainity_threshold_for_using_nn:
predicted_route = route["majority_voted_route"]You can add your own fallback flow in 2 ways:
a.) Add your own thresholds:
query_router = RouteFinder(<your_route0x_model_path>,
use_calibrated_head= True,
model_confidence_threshold_for_using_outlier_head = <your_value>,
model_uncertainity_threshold_for_using_nn= <your_value>
)b.) Add your custom logic set return_raw_scores = True and do post-hoc. if you are wondering why this might be useful. There are few datasets where outliers are not a concern so you can entirely ignore the LOF/IF head's output and only use the classifier prediction + uncertainity routing based on NNs.
How can you come up with sensible values for model_confidence_threshold_for_using_outlier_head and model_uncertainity_threshold_for_using_nn for your dataset/domain ?
We have added an experimental feature to offer a confidence_trend (confidence_trend.png in your route0x model folder), which can give a good idea as what should be these values.
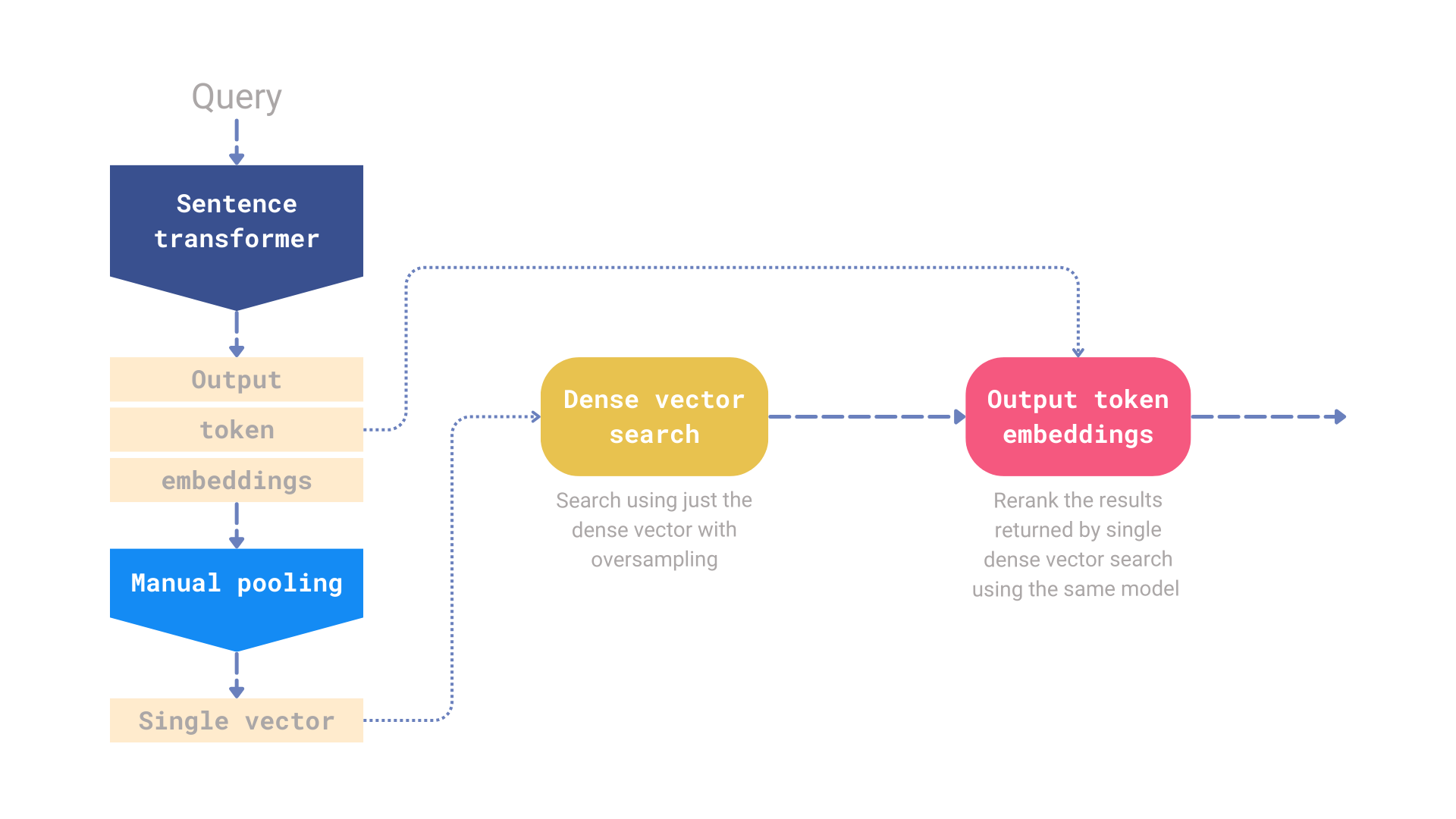
What is use_multivec_reranking and how it works ?
You can read more on this here in this awesome work by Kacper Łukawski. We took the basic idea and repurposed it. It can lift your overall peformance for a small tradeoff in latency.
image courtesy: qdrant website
Take all these numbers as sensible defaults which (surprisingly) works well across datasets, but at the same time be sure to experiment for your usecase as model training is a subjective and nuanced endeavour. Small tweaks to make or break peformance for your usecase.
'loss_funct_name': 'PairwiseArcFaceFocalLoss', # If you need Large Angular Margin + Scale between your routes.
'llm_name': 'llama3.1', # Use local or hosted LLMs. For hosted option, use provider given model names as-is.
'min_samples': 12, # Recommended.
'samples_per_route': 30, # Recommended, trying 50 can help in some cases.
'expected_oos_proportion': 0.1, # Unless you have extra domain knowledge on OOS dont touch this. if you dont except any OOS use 0.01.
'nn_for_oos_detection': 10, # # Unless you have extra domain knowledge on OOS dont touch this. if you dont except any OOS use 5.
'model_name': 'sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2',# Recommended english use-cases.
'add_additional_invalid_routes': False, # enable to stop specific intents like chitchat/profanity
"invalid_routes": ["gibberish", "mojibake", "chitchat", "non-english", "profanity"],
'instruct_llm': '' # To send additional instructions for better synthetic data gen. 'use_calibrated_head': # Default is False, Try both
'return_raw_scores': # Default is False, Try True for using custom fallback flow.
'use_multivec_reranking': # False, Try True for squeezing extra fallback performance for a tiny extra latency.
'max_length': 24, # If use_multivec_reranking = False, 24 is good, else use longer based on your median query token size.
'model_confidence_threshold_for_using_outlier_head': 0.9, # Recommended, (See "How it works" for more)
'model_uncertainity_threshold_for_using_nn': 0.5, # Recommended, (See "How it works" for more){
'train_path': None,
'eval_path': None,
'model_name': 'sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2',
'epochs': 1,
'max_steps': 100,
'batch_size': 16,
'output_dir': 'output',
'seed': 1234,
'lr': 2e-05,
'loss_funct_name': 'PairwiseArcFaceFocalLoss',
'warmup_proportion': 0.05,
'min_samples': 12,
'samples_per_route': 50,
'routes': None,
'route_template': '{}',
'domain': 'personal assistant',
'llm_name': 'llama3.1',
'instruct_llm': '',
'enable_id_oos_gen': True,
'enable_synth_data_gen': True,
'max_query_len': 24,
'hf_dataset': None,
'label_column': 'label',
'text_column': 'text',
'oos_label': 'NO_NODES_DETECTED',
'add_additional_invalid_routes': False,
'invalid_routes': ['gibberish',
'mojibake',
'chitchat',
'non-english',
'profanity'],
'expected_oos_proportion': 0.1,
'nn_for_oos_detection': 10,
'skip_eval': False,
'only_oos_head': False,
'add_typo_robustness': False,
'fallback_samples_per_route': 30,
'device': 'cuda:0',
'do_quantise': False,
'local_llm_host': 'http://localhost:11434',
'HOSTED_LLM_FAMILIES': {'openai': ['gpt'],
'anthropic': ['claude'],
'google': ['gemini']}
} {
'pooling_strategy': 'mean',
'labels_dict': {},
'metadata_dict':{},
'multi_vec_embs': '/content/route0x_sof_model/token_embeddings.npz',
'oos_label': 'NO_NODES_DETECTED',
'max_length': 24,
'model_confidence_threshold_for_using_outlier_head': 0.9,
'model_uncertainity_threshold_for_using_nn': 0.5,
'nn_for_fallback': 5
}- Integrate distilabel ?
- Integrate DSPy or AdalFlow for streamlining LLM prompt integrations ?
- Run identify best non-english base model and test on few datasets (should be straight-jacket).
- Implement typo robustness for queries.
- Fill-in other LLM providers.
- Experimental
- Identifying Confidence and Uncertainity thresholds to use fallback mechanism using Elbow/Knee locator.
- Generating a test set quickly check the route0x outputs.
On Low shot regime and domains
- Low-shot regime (+ 100 steps) demonstrated works well for closed-domain TODS/GODS systems at any granularity.
- But this WON'T work for open-domain datasets like ORCAS-I or Similar web queries. Even upgrading Low to Few shot won't help either.
- For open-domain datasets you need to switch vanilla supervised fine-tuning.
- Curious souls can compare ORCAS-I FS performance (100 samples / route) on Route0x vs Semantic Router in benchmarks folder.
On LLMS
- For Local LLMs tested only on llama3.x.
- For hosted LLMs tested only on OAI GPT.x.
- While theoretically any LLM should work, prompt faithfulness needs to verified.
- Will be added shortly