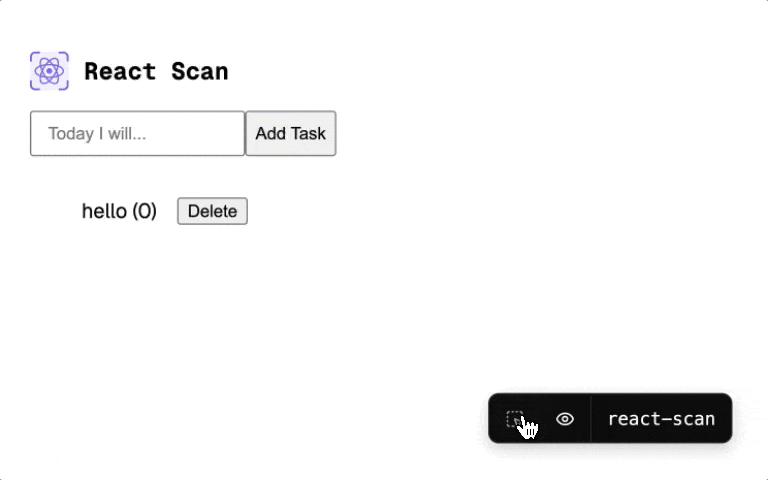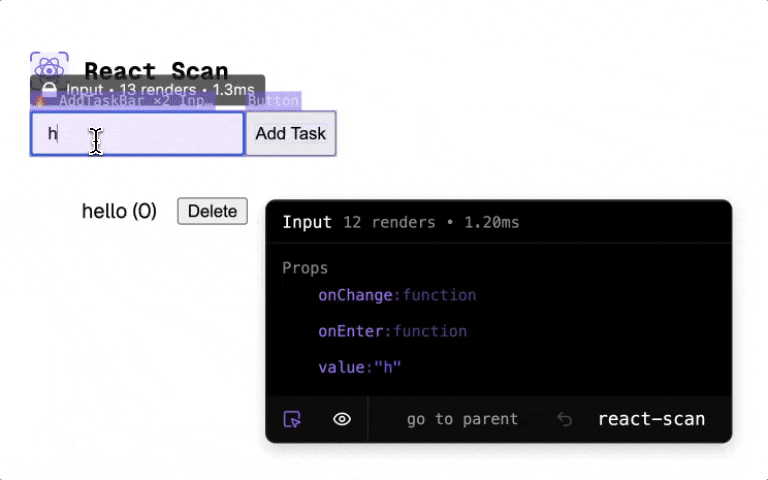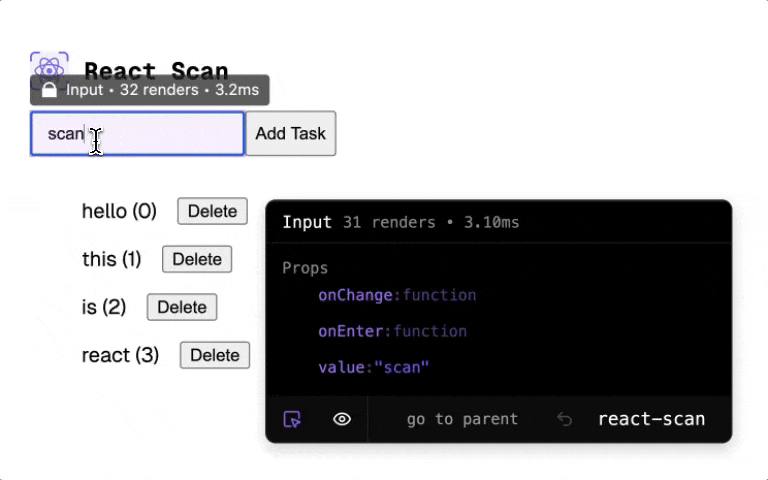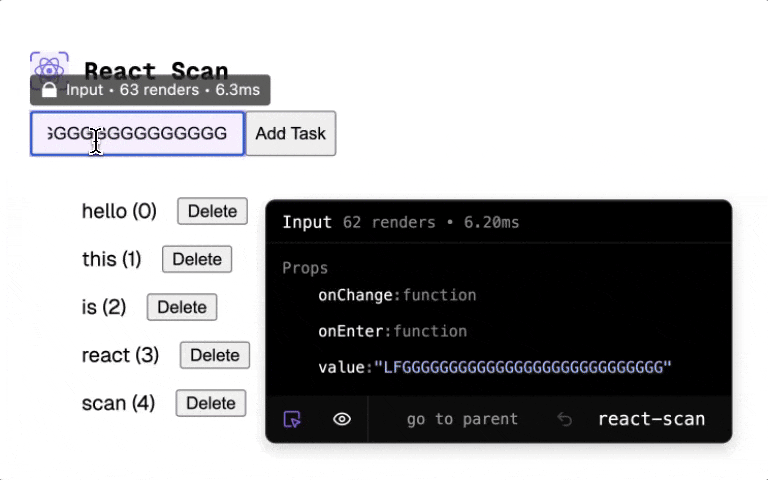
React Scan automatically detects performance issues in your React app.
Previously, tools like:
<Profiler />required lots of manual changes- Why Did You Render? lacked simple visual cues
- React Devtools didn't have a simple, portable, and programmatic API
React Scan attempts to solve these problems:
- It requires no code changes – just drop it in
- It highlights exactly the components you need to optimize
- Use it via script tag, npm, CLI, you name it!
Trusted by engineering teams at:
Important
Want to monitor issues in production? Check out React Scan Monitoring!
Add this script to your app:
<!-- import this BEFORE any scripts -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-scan/dist/auto.global.js"></script>Examples:
Next.js (pages)
Add the script tag to your pages/_document.tsx:
import { Html, Head, Main, NextScript } from 'next/document';
export default function Document() {
return (
<Html lang="en">
<Head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-scan/dist/auto.global.js"></script>
{/* rest of your scripts go under */}
</Head>
<body>
<Main />
<NextScript />
</body>
</Html>
);
}Next.js (app)
Add the script tag to your app/layout.tsx:
export default function RootLayout({
children,
}: {
children: React.ReactNode
}) {
return (
<html lang="en">
<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-scan/dist/auto.global.js" async />
{/* rest of your scripts go under */}
</head>
<body>{children}</body>
</html>
)
}Vite / Create React App
Add the script tag to your index.html:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-scan/dist/auto.global.js"></script>
<!-- rest of your scripts go under -->
</head>
<body>
<!-- ... -->
</body>
</html>If you want to install the Chrome extension, follow the guide here, or React Native support, see here.
If you need a programmatic API to debug further, install via NPM instead:
npm install react-scanThen, in your app, import this BEFORE react. This must run in a client context (e.g. not in a server component):
import { scan } from 'react-scan'; // import this BEFORE react
import React from 'react';
if (typeof window !== 'undefined') {
scan({
enabled: true,
log: true, // logs render info to console (default: false)
});
}Looking for React Native?
If you don't have a localv version of the site, you can use the CLI. This will spin up an isolated browser instance which you can interact or use React Scan with.
npx react-scan@latest http://localhost:3000
# you can technically scan ANY website on the web:
# npx react-scan@latest https://react.devYou can add it to your existing dev process as well. Here's an example for Next.js:
{
"scripts": {
"dev": "next dev",
"scan": "next dev & npx react-scan@latest localhost:3000"
}
}Options
export interface Options {
/**
* Enable/disable scanning
*
* Please use the recommended way:
* enabled: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development',
*
* @default true
*/
enabled?: boolean;
/**
* Include children of a component applied with withScan
*
* @default true
*/
includeChildren?: boolean;
/**
* Enable/disable geiger sound
*
* @default true
*/
playSound?: boolean;
/**
* Log renders to the console
*
* @default false
*/
log?: boolean;
/**
* Show toolbar bar
*
* @default true
*/
showToolbar?: boolean;
/**
* Render count threshold, only show
* when a component renders more than this
*
* @default 0
*/
renderCountThreshold?: number;
/**
* Clear aggregated fibers after this time in milliseconds
*
* @default 5000
*/
resetCountTimeout?: number;
/**
* Maximum number of renders for red indicator
*
* @default 20
* @deprecated
*/
maxRenders?: number;
/**
* Report data to getReport()
*
* @default false
*/
report?: boolean;
/**
* Always show labels
*
* @default false
*/
alwaysShowLabels?: boolean;
/**
* Animation speed
*
* @default "fast"
*/
animationSpeed?: 'slow' | 'fast' | 'off';
/**
* Smoothly animate the re-render outline when the element moves
*
* @default true
*/
smoothlyAnimateOutlines?: boolean;
/**
* Track unnecessary renders, and mark their outlines gray when detected
*
* An unnecessary render is defined as a component re-rendering with no change to the component's corresponding dom subtree (e.g. a component re-rendered, but nothing in the components UI did not change)
*
* @default true
* @warning tracking unnecessary renders can add meaningful overhead to react-scan
*/
trackUnnecessaryRenders?: boolean;
onCommitStart?: () => void;
onRender?: (fiber: Fiber, render: Render) => void;
onCommitFinish?: () => void;
onPaintStart?: (outlines: PendingOutline[]) => void;
onPaintFinish?: (outlines: PendingOutline[]) => void;
}scan(options: Options): Imperative API to start scanninguseScan(options: Options): Hook API to start scanningwithScan(Component, options: Options): Whitelist a specific component, do not scan other componentsgetReport(): Get a report of all the renderssetOptions(options: Options): void: Set options at runtimegetOptions(): Get the current optionsonRender(Component, onRender: (fiber: Fiber, render: Render) => void): Hook into a specific component's rendersgetRenderInfo(Component): Get the render info for a specific component
React can be tricky to optimize.
The issue is that component props are compared by reference, not value. This is intentional – this way rendering can be cheap to run.
However, this makes it easy to accidentally cause unnecessary renders, making the app slow. Even in production apps, with hundreds of engineers, can't fully optimize their apps (see GitHub, Twitter, and Instagram).
This often comes down to props that update in reference, like callbacks or object values. For example, the onClick function and style object are re-created on every render, causing ExpensiveComponent to slow down the app:
<ExpensiveComponent onClick={() => alert('hi')} style={{ color: 'purple' }} />React Scan helps you identify these issues by automatically detecting and highlighting renders that cause performance issues. Now, instead of guessing, you can see exactly which components you need to fix.
Want monitor issues in production? Check out React Scan Monitoring!
Q: Why this instead of React Devtools?
React Devtools aims to be a general purpose tool for React. However, I deal with React performance issues every day, and React Devtools doesn't fix my problems well. There's a lot of noise (no obvious distinction between unnecessary and necessary renders), and there's no programmatic API. If it sounds like you have the same problems, then React Scan may be a better choice.
Also, some personal complaints about React Devtools' highlight feature:
- React Devtools "batches" paints, so if a component renders too fast, it will lag behind and only show 1 every second or so
- When you scroll/resize the boxes don't update position
- No count of how many renders there are
- I don't know what the bad/slow renders are without inspecting
- The menu is hidden away so it's annoying to turn on/off, user experience should be specifically tuned for debugging performance, instead of hidden behind a profiler/component tree
- No programmatic API
- It's stuck in a chrome extension, I want to run it anywhere on the web
- It looks subjectively ugly (lines look fuzzy, feels sluggish)
- I'm more ambitious with react-scan (see our roadmap)
Q: React Native wen?
Soon :)
Q: Chrome Extension wen?
Soon :)
Want to try it out? Check the our demo.
Looking to contribute back? Check the Contributing Guide out.
Want to talk to the community? Hop in our Discord and share your ideas and what you've build with React Scan.
Find a bug? Head over to our issue tracker and we'll do our best to help. We love pull requests, too!
We expect all contributors to abide by the terms of our Code of Conduct.
→ Start contributing on GitHub
- Scan only for unnecessary renders ("unstable" props)
- Scan API (
withScan,scan) - Cleanup config options
- Chrome extension (h/t @biw)
- Mode to highlight long tasks
- Add context updates
- Expose primitives / internals for advanced use cases
- More explicit options override API (start log at certain area, stop log, etc.)
- Don't show label if no reconciliation occurred ("client renders" in DevTools)
- "global" counter using
sessionStorage, aggregate count stats instead of immediate replacement - Give a general report of the app's performance
- Select areas of the screen to scan
- Report should include all renders
- heatmap decay (stacked renders will be more intense)
- Investigate components (UI allowlist)
- Offscreen canvas on worker thread
- UI for turning on/off options
- “PageSpeed insights” for React
- CLI
- React Native support
- Cleanup API reference
- Name / explain the actual problem, docs
- Simple FPS counter
- Runtime version guarding
- React as peer dependency (lock version to range)
- Add a funny mascot, like the "Stop I'm Changing" dude
React Scan takes inspiration from the following projects:
- React Devtools for the initial idea of highlighting renders. We chose to diverge from this to provide a better developer experience
- Million Lint for scanning and linting approaches
- Why Did You Render? for the concept of hijacking internals to detect unnecessary renders caused by "unstable" props
React Scan is MIT-licensed open-source software by Aiden Bai, Million Software, Inc., and contributors: