Given a weighted undirected connected graph with n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi, weighti] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between nodes ai and bi. A minimum spanning tree (MST) is a subset of the graph's edges that connects all vertices without cycles and with the minimum possible total edge weight.
Find all the critical and pseudo-critical edges in the given graph's minimum spanning tree (MST). An MST edge whose deletion from the graph would cause the MST weight to increase is called a critical edge. On the other hand, a pseudo-critical edge is that which can appear in some MSTs but not all.
Note that you can return the indices of the edges in any order.
Example 1:
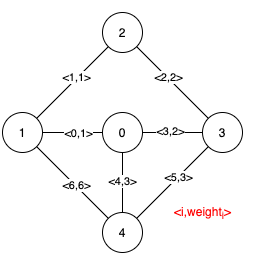
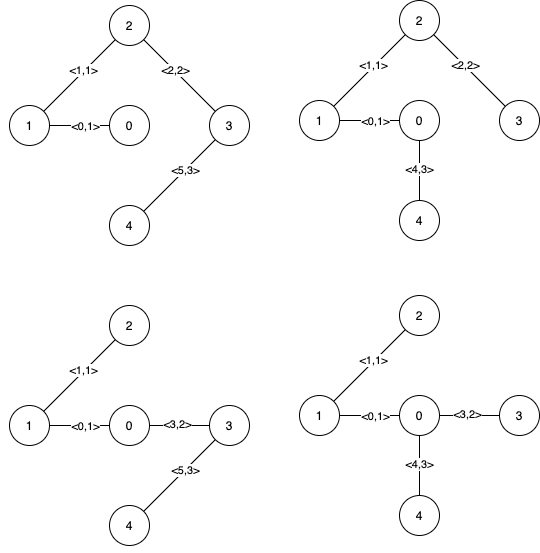
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,2],[0,3,2],[0,4,3],[3,4,3],[1,4,6]] Output: [[0,1],[2,3,4,5]] Explanation: The figure above describes the graph. The following figure shows all the possible MSTs:Notice that the two edges 0 and 1 appear in all MSTs, therefore they are critical edges, so we return them in the first list of the output. The edges 2, 3, 4, and 5 are only part of some MSTs, therefore they are considered pseudo-critical edges. We add them to the second list of the output.
Example 2:
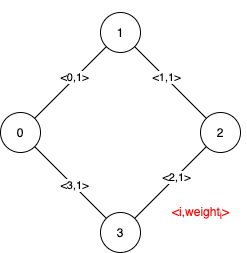
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[0,3,1]] Output: [[],[0,1,2,3]] Explanation: We can observe that since all 4 edges have equal weight, choosing any 3 edges from the given 4 will yield an MST. Therefore all 4 edges are pseudo-critical.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= min(200, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i].length == 30 <= ai < bi < n1 <= weighti <= 1000- All pairs
(ai, bi)are distinct.
[Union Find] [Graph] [Sorting] [Minimum Spanning Tree] [Strongly Connected Component]