Given a binary tree root, return the maximum sum of all keys of any sub-tree which is also a Binary Search Tree (BST).
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
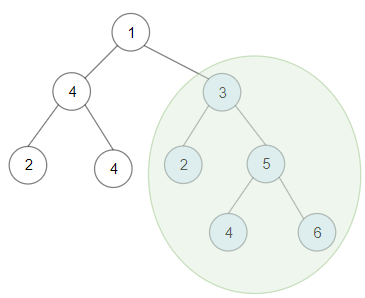
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,4,3,2,4,2,5,null,null,null,null,null,null,4,6] Output: 20 Explanation: Maximum sum in a valid Binary search tree is obtained in root node with key equal to 3.
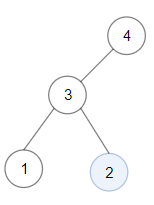
Example 2:
Input: root = [4,3,null,1,2] Output: 2 Explanation: Maximum sum in a valid Binary search tree is obtained in a single root node with key equal to 2.
Example 3:
Input: root = [-4,-2,-5] Output: 0 Explanation: All values are negatives. Return an empty BST.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 4 * 104]. -4 * 104 <= Node.val <= 4 * 104
[Dynamic Programming] [Tree] [Depth-First Search] [Binary Search Tree] [Binary Tree]