Welcome to Hackintosh installation jog learning. In this part, you will learn the basics of Hackintosh.
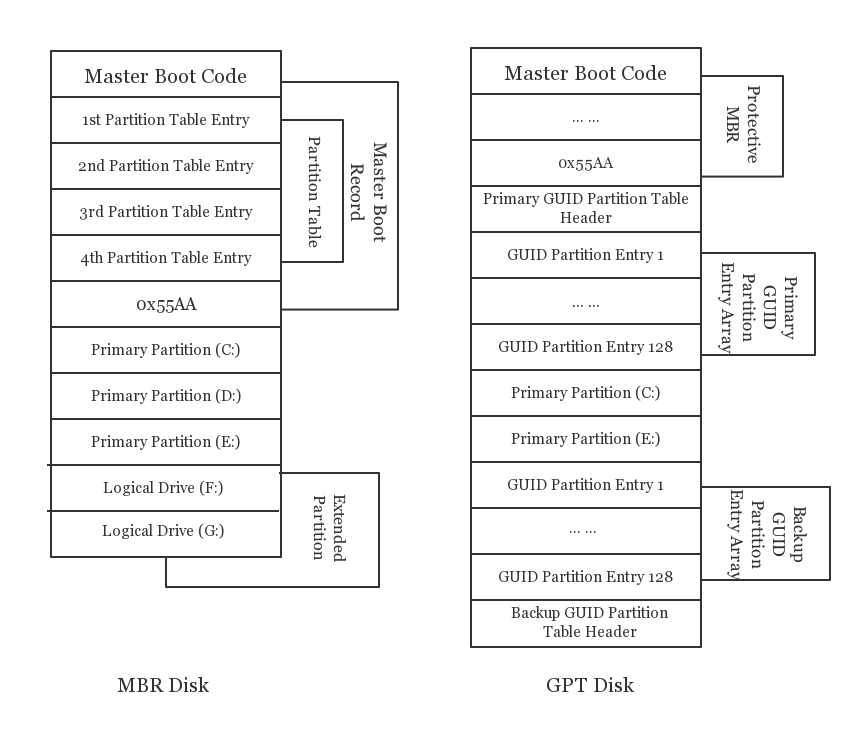
When you are setting up a new disk on an operation system, you’ll be asked whether you want to use MBR (Master Boot Record) or GPT (GUID Partition Table). MBR and GPT are two different ways of storing the partitioning information on a drive. This information includes where partitions start and begin, so your operating system knows which sectors belong to each partition and which partition is bootable. This is why you have to choose MBR or GPT before creating partitions on a drive. It's the first step to install a operation system.
We can get some informations from Wikipedia about GPT:
GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a standard for the layout of the partition table on a physical storage device used in a desktop or server PC, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, using globally unique identifiers (GUID). Although it forms a part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard (Unified EFI Forum proposed replacement for the PC BIOS), it is also used on some BIOS systems because of the limitations of master boot record (MBR) partition tables, which use 32 bits for storing logical block addresses (LBA) and size information on a traditionally 512-byte disk sector.
And MBR:
A master boot record (MBR) is a special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept of MBRs was publicly introduced in 1983 with PC DOS 2.0.
The MBR holds the information on how the logical partitions, containing file systems, are organized on that medium. The MBR also contains executable code to function as a loader for the installed operating system—usually by passing control over to the loader's second stage, or in conjunction with each partition's volume boot record (VBR). This MBR code is usually referred to as a boot loader.
If you want to know something more about hard disk partitions, please see here.
Actually, MBR and GPT also determine the style of the disk between MBR and GPT. After initializing it, we can call a disk as MBR disk or GPT disk. The two different styles of disk own different schemes to manage the partitions on a disk. The differences between them are caused by the rapid development of the information age and the older scheme shows more and more disadvantages.
The organization of the partition table in the MBR limits the maximum addressable storage space of a disk to 2 TB (232 × 512 bytes). And it only supports up to 4 primary partitions, or 3 primary partitions and 1 extended partition combination. However, with the progress of the times, larger storage devices need to be applied to the computer field. Therefore, the MBR-based partitioning scheme is in the process of being superseded by the GUID Partition Table (GPT) scheme in new computers because of GPT partition table disk supports a volume up to 2^64 blocks in length e.g. for disks with 512-byte sectors, that would be 9.44 ZB – zettabytes, 1 ZB is 1 billion terabytes, and the ability to have up to 128 primary partitions. A GPT can coexist with an MBR in order to provide some limited form of backward compatibility for older systems.
For our hackintosh installation, we recommend using a GPT instead of using a MBR. So, how to change a MBR to GPT?
Nearly all computers made after 2012 boot UEFI as opposed to the older standard known as "Legacy". These computers require an ESP partition to boot. ESP stands for EFI System Partition and is formatted with the FAT32/FAT16 file system. The ESP is responsible for storing EFI bootloaders and other utilities used by the firmware at startup. If you were to accidentally delete this partition, your system will no longer be able to boot. For security, the ESP is hidden since it has no drive letter.
If you have Pre-installed Windows, your ESP is 100MB by default. If your hard drive was initialized as GUID Partition table (GPT) partition style, it will generate an EFI system partition automatically after installing Windows or Mac operating system (OS).
The definition of ESP in Wikipedia is:
The EFI system partition (ESP) is a partition on a data storage device (usually a hard disk drive or solid-state drive) that is used by computers adhering to the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). When a computer is booted, UEFI firmware loads files stored on the ESP to start installed operating systems and various utilities. An ESP needs to be formatted with a file system whose specification is based on the FAT file system and maintained as part of the UEFI specification; therefore, the file system specification is independent from the original FAT specification.
Remember, for Hackintosh installations, a 100MB ESP partition will not work. Your ESP partition must be at least 200MB to boot into macOS to use gdisk to create Apple patition styles. You can combine the ESP partition with the MSR partition to get a larger ESP paratition if you have Pre-installed Windows
To create an EFI partition, you can use a WinPE (booted from a usb bootable media). You can find more information here: how to build a winPE in your usb devices.
Assuming that we have a clean disk to install macOS on, the first thing you need to do is partition your drive. If you want to install Windows first, you'll need to create an ESP, a MSR (Microsoft Reserved Partition) and partitions for each operating system. You can follow the steps below to do this. (WARNING: This will erase anything you current have on your drive):
- Boot into winPE and open a command tool (CMD).
- Enter:
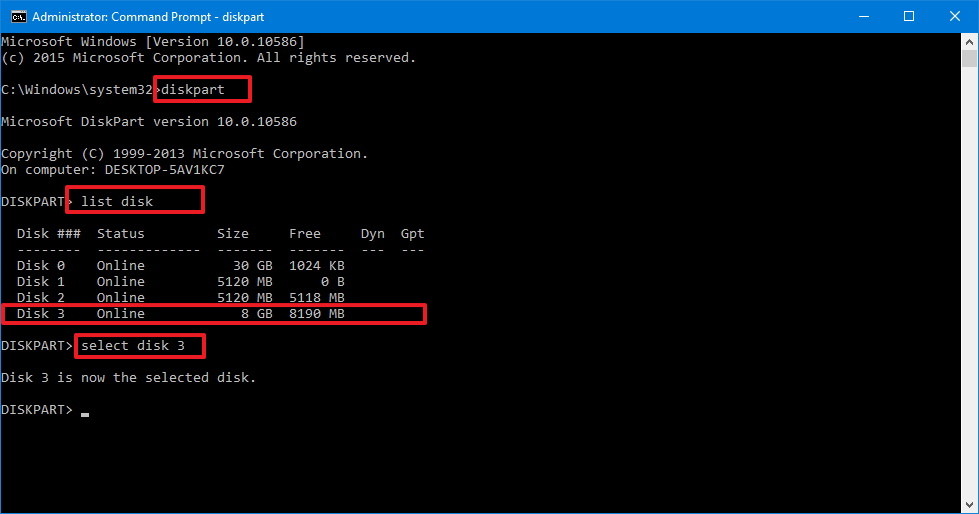
diskpartto start a disk tool (run cmd under administration). - Enter:
list diskto list all the disks in your computer. - Enter:
select disk xto select the disk you want to rebuild. (xis the number of your disk) - Enter:
cleanto clean all the disk. - Enter:
convert gptto convert this disk to a GPT form (if you are already a GPT form, you can skip this step). - Enter:
create partition EFI size=200to build a 200M ESP partition. - Enter:
format quick fs=fat32 label="System"to form this partition. - Optional:
create partition msr size = 128you can use this to create a MSR (Microsoft Reserved Partition) partition.
You can also use some disk tool (with GUI) to build a EFI partition. After convert gpt you can also:
- Close cmd window, open DiskGenius or something like this (disk tool).
- Create a new partition
An ESP can also be created through Disk Utility on macOS if you don't want to install Windows before macOS.
- Open Terminal.
- Enter:
diskutil listand find the disk you want to partition. - Enter:
diskutil partitionDisk /dev/diskX 2 MBR FAT32 "EFI" 200Mi HFS+J "macOS" Rreplace diskX with the disk you want to partition.
Note: The ESP partition can be created anywhere on a disk (as the computer can find the bootloaders). You can ultimately create these partitions in any order you'd like.