- Build a backend for our todo list application
- Short introduction into RESTful architecture
- Use Node.js express server for create, read, update, delete (CRUD) operations
- MongoDB as data storage
- End2end, integration and unit tests
- Asynchronous data fetching on the frontend via redux-thunk
In the last lesson, the data was just kept in memory and not persisted. In this lecture, we will create a Node.js backend and store the data in a non-relational database (MongoDB).
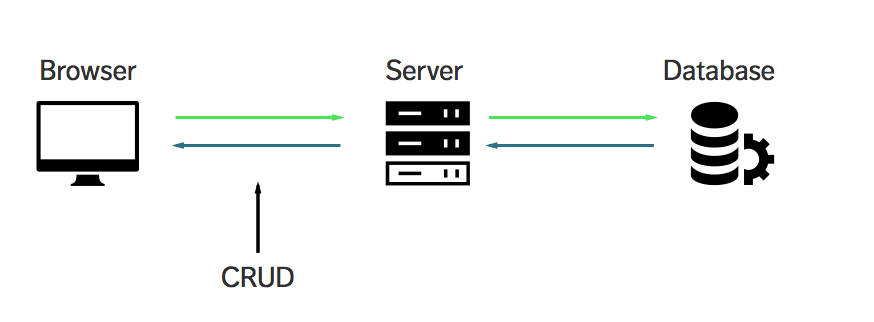
The target architecture will be the following:
Start by cloning the repository:
git clone https://github.com/msd-code-academy/lessons.git
git pullThe files relevant for this lesson will be located in the folder lesson-7. It consists of a Node.js server part (folder server) as well as a React/Redux client part (folder todos).
Run the following commands to install the necessary packages:
cd lesson-7
cd server
npm install
cd todos
npm installThere are several parts of the code which are marked by TODO which we will fill in the exercises. As a homework, you can further extend the solution. During the course, please make sure you are connected to the Guest WIFI to be able to connect to the database which is hosted on an online service (it is not accessible from the company network).
REST stand for Representational state transfer. Basically, it allows access to textual representations (e.g., JSON or XML) of web resources (identified via URI) using a standard set of pre-defined HTTP methods:
- GET - represents "read" operations. Used for retrieving resources and collections. It is a "safe" operation - it does not modify data on the server.
- POST - "write" operations. Used for creating new resources.
- PUT - "write" operations. Used for updating existing resources.
- PATCH - partial "write" operations. Used for performing partial updates. Unlike the PUT method, where the whole resource should be provided, with the PATCH method you provide only part of the resource to be changed - for example, a specific property.
- DELETE - "delete" operations. Used for deleting resources.
Please note that the REST architecture is a client-server model which has some important constraints like statelessness (no client-context stored on server), cacheability and uniform interface (REST-service interfaces follows basic design principles) - see references for more details.
Our resource will be a list of todo items. We will support the following operations:
- /todos
- GET: list all todo items
- /todos/:id
- POST: create todo item with id (Create)
- GET: retrieve todo item with id (Read)
- PUT: update todo item with id (Update)
- DELETE: delete todo item with id (Delete)
- HTTP/1.1 Specification (https://www.w3.org/Protocols/)
- REST API Tutorial (http://www.restapitutorial.com/)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Representational_state_transfer
Node.js is a cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment that is built on the Chrome V8 engine. It is used to execute JavaScript code on the server-side. It is based on modules which are managed by a package manager such as npm.
It operates on a single thread and the runtime is asynchronous and event-driven. This is important to keep in mind and not to do any blocking operations such as synchronous I/O or long-running functions. As long as operations are performed asynchronously, many requests can be handled concurrently (but not in parallel).
Express is a very popular Node.js application server framework. It creates a layer over the native HTTP and Node.js functionality. It is very extensible and is based on middlewares that handle the request and create the response (for example error handling, request parsing, create json response, ...). An express application is basically a chain of middleware function calls. In this exercise, we will use it to build our RESTful api.
- https://nodejs.org/en
- https://www.npmjs.com
- https://softwareengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/190719/the-difference-between-concurrent-and-parallel-execution
- https://expressjs.com
- http://expressjs.com/en/guide/using-middleware.html
- https://zellwk.com/blog/crud-express-mongodb
- Implement CRUD endpoints (see
server/app.js)
MongoDB is a NoSQL database which stores JSON documents and schemas. It supports features like ad-hoc queries, indices, load balancing and replication. You can access it from Node.js application using the mongodb package.
Documents are organized into collections and contain fields:
For the purpose of this lecture, we use a cloud instace created on https://www.mongodb.com/cloud/atlas. As a first step, edit the file server/config.js and put there your own database name in the variable MONGO_DB_NAME (e.g., put there your last name).
- https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/crud
- https://www.w3schools.com/nodejs/nodejs_mongodb.asp
- https://www.mongodb.com
- Implement CRUD operations and make tests pass (see
server/api.js). Run tests usingnpm run test
As a test runner we use mocha as a test runner and chai for assertions.
In this exercise we will cover three different kinds of tests:
- End2end tests which will call the endpoints on http://localhost:8080 (file
e2e-test/e2e.js). For querying the endpoints we use the module supertest. - Integration tests which will test the api functions together with the database (file
test/api.js) - Unit tests which independently test certain functions (file
test/requestHandler.js). The api calls are mocked using sinon and chai-spies.
- https://mochajs.org
- http://chaijs.com
- https://github.com/visionmedia/supertest
- http://sinonjs.org
- http://chaijs.com/plugins/chai-spies
- Add unit test to test the error case of RequestHandler (see
test/requestHandler.js). Hint: usesinon.stub().returnsPromise().rejects(testError)
In the last lesson (lesson 6), Redux was used for handling the state of todo items. The state was only kept locally in memory. In this lesson, we want to perform these actions on our backend. Since the calls to the backend are asynchronous, we need a helper library for that. Redux by default supports only synchronous actions.
In this exercise, we will use redux-thunk do handle the asynchronous calls to our backend.
- Add error handling if a request to the backend fails (for example, display a message for the user)
- Add a spinner while waiting for responses from the backend (see lesson 4)
- Implement a search-box to search for todo-items. Create a new endpoint on server-side to perform search operations. Use built-in MongoDB features for that purpose.
- Add a new summary endpoint on server-side to provide data for the summary page (number of items, most recent items). Like this, you do not need to fetch the whole list of items when you open the summary page.
- Implement further tests for the backend. For example, cover each endpoint by an end2end test.
- Add a login functionality to your app. Hint - add a /login endpoint and use a session cookie (see for example last years lession - https://github.com/msd-code-academy/05-cinema-portal-with-server/blob/master/server/app.js)