 ](https://flutter.dev/docs/development/packages-and-plugins/favorites)
-[Freezed] 세계에 오신걸 환영합니다. [Freezed]는 data-classes/unions/cloning를 위한 코드 생성기입니다.
+[Freezed]에 오신 것을 환영합니다. 이 라이브러리는 데이터 클래스, 태그드 유니온(tagged unions), 중첩 클래스, 그리고 객체 복제(cloning)를 위한 또 하나의 코드 생성기입니다.
-# Freezed가 만들어진 이유
+# 3.0.0으로 마이그레이션
-Dart는 훌륭한 언어입니다. 하지만 "모델"을 정의하는 과정은 번거롭습니다.
+2.0.0에서 3.0.0으로 마이그레이션하려면 [변경 로그](https://github.com/rrousselGit/freezed/blob/master/packages/freezed/CHANGELOG.md#300---2025-02-25)와 [마이그레이션 가이드](https://github.com/rrousselGit/freezed/blob/master/packages/freezed/migration_guide.md)를 참조하세요.
-모델을 정의하려면 아래와 같은 작업이 필요합니다:
+# 동기
-생성자와 속성 정의하기
-`toString`, `operator ==`, `hashCode` 오버라이드
-객체를 복사하기 위한 `copyWith` 메서드 구현
-직렬화 및 역직렬화 처리
-게다가 Dart에는 `union types`, `pattern-matching` 같은 기능이 없습니다.
+Dart는 훌륭한 언어지만, '모델'을 정의하는 것은 지루한 작업이 될 수 있습니다. 다음과 같은 작업들이 필요합니다:
-이 모든 것을 직접 구현하려면 코드가 수백 줄로 늘어날 수도 있습니다. 이런 작업은 오류를 만들기 쉽고, 모델의 가독성을 떨어뜨릴 수 있습니다.
+- 생성자(constructor)와 프로퍼티(properties) 정의
+- `toString`, `operator ==`, `hashCode` 오버라이드
+- 객체 복제를 위한 `copyWith` 메서드 구현
+- 직렬화/역직렬화(de/serialization) 처리
-[Freezed]는 이런 부분들을 대신 처리해줌으로써 위와 같은 문제를 해결하고, 사용자가 모델 정의에 집중할 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
+이 모든 것을 구현하는 데에는 수백 줄의 코드가 필요할 수 있으며, 이는 오류가 발생하기 쉽고 모델의 가독성을 크게 해칩니다.
-| Freezed 사용 전 | Freezed 사용 후 |
-| ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-|  |  |
+Freezed는 이 대부분의 작업을 대신 구현하여, 개발자가 모델의 정의에만 집중할 수 있도록 돕습니다.
+
+| 이전 | 이후 |
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| 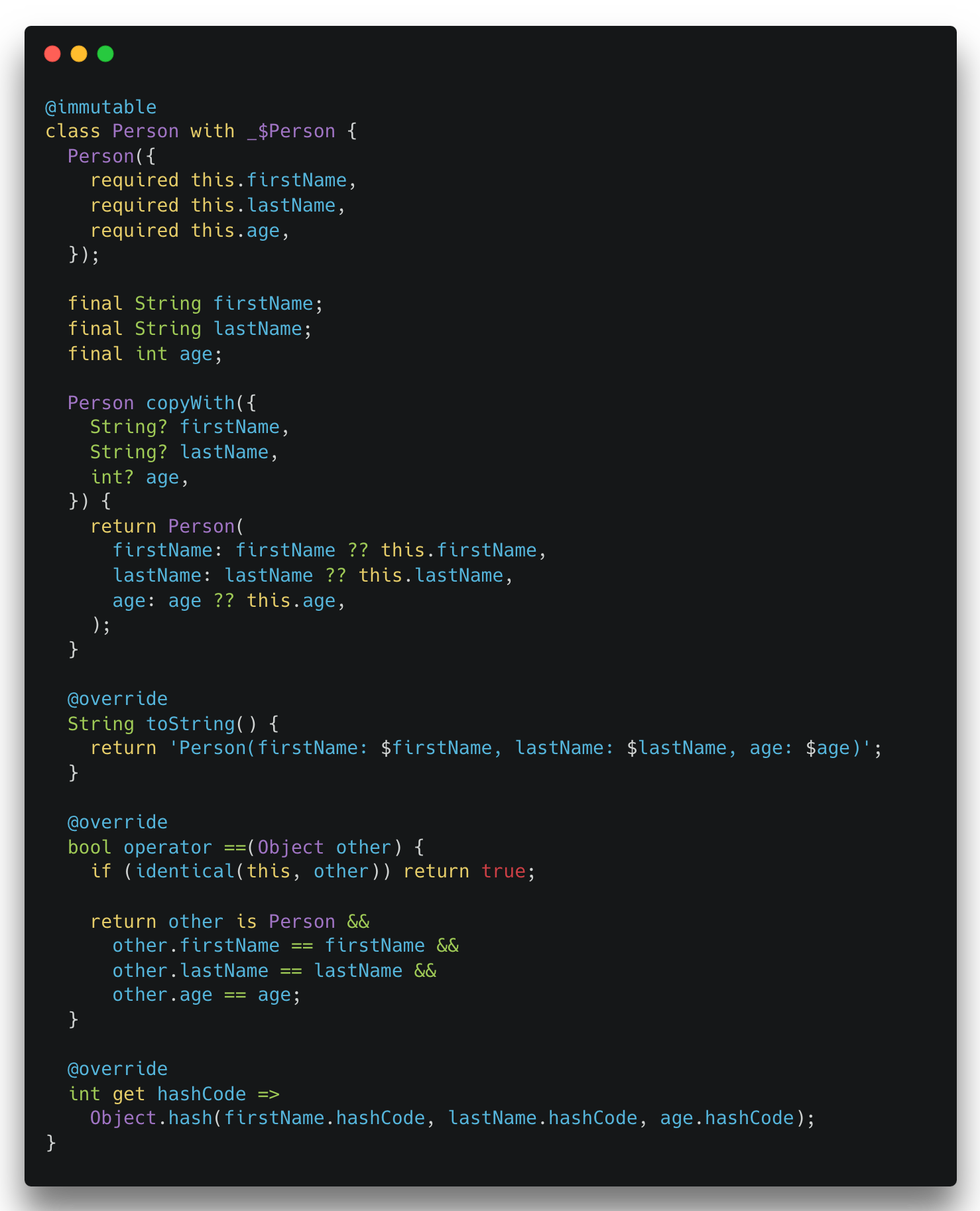 | 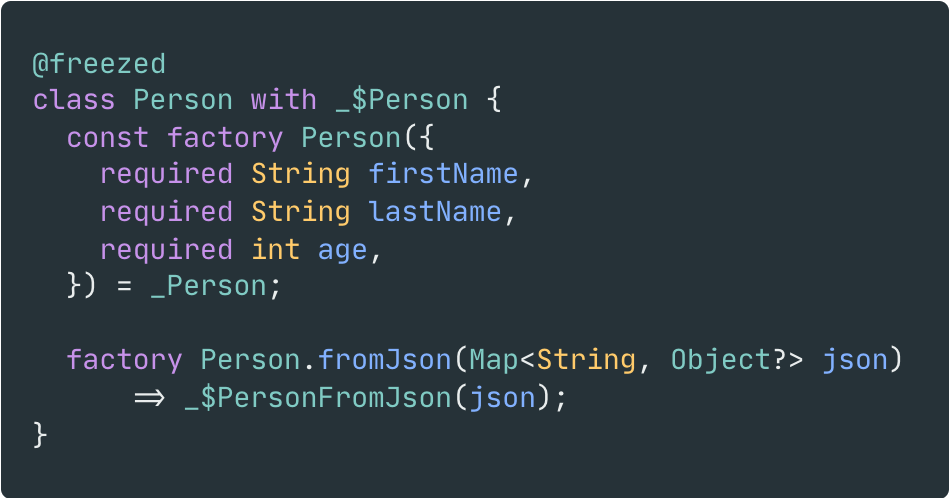 |
# 목차
-- [Freezed를 만들게된 이유](#Freezed를-만들게된-이유)
+- [3.0.0으로 마이그레이션](#300으로-마이그레이션)
+- [동기](#동기)
- [목차](#목차)
-- [사용방법](#사용방법)
- - [설치하기](#설치하기)
- - [invalid_annotation_target 경고 및 생성파일의 경고를 비활성 시키기](#invalid_annotation_target-경고-및-생성파일의-경고를-비활성-시키기)
- - [generator 실행하기](#generator-실행하기)
- - [Freezed를 사용하여 모델 생성하기](#Freezed를-사용하여-모델-생성하기)
- - [immutable 클래스 대신 mutable 클래스 정의하기](#Immutable-클래스-대신-Mutable-클래스-정의하기)
- - [Lists/Maps/Sets의 변경 허용하기](#listsmapssets의-변경-허용하기)
- - [copyWith의 작동방식](#copyWith의-작동방식)
- - [더 나아가기: 깊은복사](#더-나아가기-깊은복사)
- - [모델에 getters 와 메서드 추가하기](#모델에-getters와-메서드-추가하기)
- - [Asserts](#asserts)
- - [기본 값](#기본-값)
- - [데코레이터와 코멘트](#데코레이터와-코멘트)
- - [Union Types에서 Mixin 및 Interface 사용하기](#Union-Types에서-Mixin-및-Interface-사용하기)
+- [사용 방법](#사용-방법)
+ - [설치](#설치)
+ - [invalid_annotation_target 경고 및 생성된 파일의 경고 비활성화](#invalid_annotation_target-경고-및-생성된-파일의-경고-비활성화)
+ - [생성기 실행](#생성기-실행)
+ - [Freezed를 사용하여 모델 만들기](#freezed를-사용하여-모델-만들기)
+ - [기본 생성자](#기본-생성자)
+ - [모델에 getter와 메서드 추가하기](#모델에-getter와-메서드-추가하기)
+ - [Asserts](#asserts)
+ - [기본값](#기본값)
+ - [상수가 아닌 기본값](#상수가-아닌-기본값)
+ - [클래스 확장하기](#클래스-확장하기)
+ - [불변 클래스 대신 가변 클래스 정의하기](#불변-클래스-대신-가변-클래스-정의하기)
+ - [List/Map/Set의 변경 허용하기](#listmapset의-변경-허용하기)
+ - [일반 클래스](#일반-클래스)
+ - [copyWith 동작 방식](#copywith-동작-방식)
+ - [더 나아가기: 깊은 복사(Deep copy)](#더-나아가기-깊은-복사deep-copy)
+ - [데코레이터와 주석](#데코레이터와-주석)
- [FromJson/ToJson](#fromjsontojson)
- - [fromJSON - 복수의 생성자가 있는 클래스](#fromjson---복수의-생성자가-있는-클래스)
- - [제네릭 클래스 역직렬화하기](#제네릭-클래스-역직렬화하기)
- - [Union types과 Sealed classes](#Union-types과-Sealed-classes)
- - [공유속성 Shared properties](#공유속성-Shared-properties)
- - [패턴매칭(pattern-matching)을 사용하여 비공유 속성 읽기](#패턴매칭pattern-matching을-사용하여-비공유-속성읽기)
- - [권장하지 않는 패턴매칭 메소드](#)
+ - [fromJSON - 여러 생성자를 가진 클래스](#fromjson---여러-생성자를-가진-클래스)
+ - [제네릭 클래스 역직렬화](#제네릭-클래스-역직렬화)
+ - [유니온 타입](#유니온-타입)
+ - [공유 프로퍼티](#공유-프로퍼티)
+ - [패턴 매칭을 사용하여 공유되지 않는 프로퍼티 읽기](#패턴-매칭을-사용하여-공유되지-않는-프로퍼티-읽기)
+ - [유니온 타입의 개별 클래스를 위한 Mixin과 Interface](#유니온-타입의-개별-클래스를-위한-mixin과-interface)
+ - [개별 유니온 케이스 분리하기](#개별-유니온-케이스-분리하기)
+ - [(레거시) 패턴 매칭 유틸리티](#레거시-패턴-매칭-유틸리티)
- [When](#when)
- [Map](#map)
- - [환경설정](#환경설정)
- - [특정 모델의 동작변경](#특정-모델의-동작변경)
- - [전체 프로젝트의 동작변경](#전체-프로젝트의-동작변경)
-- [Utilities](#utilities)
- - [VSCode전용 Freezed extension](#VSCode전용-Freezed-extension)
- - [IntelliJ/Android Studio전용 Freezed extension](#IntelliJAndroid-Studio전용-Freezed-extension)
- - [Sponsors](#sponsors)
+ - [설정](#설정)
+ - [특정 모델의 동작 변경하기](#특정-모델의-동작-변경하기)
+ - [전체 프로젝트의 동작 변경하기](#전체-프로젝트의-동작-변경하기)
+- [유틸리티](#유틸리티)
+ - [IDE 확장 프로그램](#ide-확장-프로그램)
+ - [VSCode용 Freezed 확장 프로그램](#vscode용-freezed-확장-프로그램)
+ - [IntelliJ/Android Studio용 Freezed 확장 프로그램](#intellijandroid-studio용-freezed-확장-프로그램)
+ - [린팅(Linting)](#린팅linting)
+ - [서드파티 도구](#서드파티-도구)
+ - [DartJ](#dartj)
+ - [스폰서](#스폰서)
-# 사용방법
+# 사용 방법
-## 설치하기
+## 설치
-[Freezed]를 사용하려면 일반적으로 [build_runner]/code-generator 설정이 필요합니다.
-먼저 [build_runner]와 [Freezed]를 `pubspec.yaml` 파일에 추가합니다.
+[Freezed]를 사용하려면 일반적인 [build_runner]/코드 생성기 설정이 필요합니다.\
+먼저, `pubspec.yaml` 파일에 [build_runner]와 [Freezed]를 추가하여 설치합니다:
-만약에 `Flutter`프로젝트를 생성하는 경우에는 아래와 같이 진행합니다.
+Flutter 프로젝트의 경우:
```console
-flutter pub add freezed_annotation
-flutter pub add dev:build_runner
-flutter pub add dev:freezed
-# fromJson/toJson 생성도 사용하려면 아래를 추가하세요:
-flutter pub add json_annotation
-flutter pub add dev:json_serializable
+flutter pub add \
+ dev:build_runner \
+ freezed_annotation \
+ dev:freezed
+# freezed로 fromJson/toJson을 생성한다면 다음도 추가하세요:
+flutter pub add json_annotation dev:json_serializable
```
-만약에 `Dart`프로젝트를 생성하는 경우에는 아래와 같이 진행합니다.
+Dart 프로젝트의 경우:
```console
-dart pub add freezed_annotation
-dart pub add dev:build_runner
-dart pub add dev:freezed
-# fromJson/toJson 생성도 사용하려면 아래를 추가하세요:
-dart pub add json_annotation
-dart pub add dev:json_serializable
+dart pub add \
+ dev:build_runner \
+ freezed_annotation \
+ dev:freezed
+# freezed로 fromJson/toJson을 생성한다면 다음도 추가하세요:
+dart pub add json_annotation dev:json_serializable
```
-이렇게 하면 3개의 패키지(freezed_annotation, build_runner, freezed)가 설치됩니다.
+이 명령어는 세 개의 패키지를 설치합니다:
-- [build_runner](https://pub.dev/packages/build_runner): `code-generators`를 실행하기 위한 도구입니다.
-- [freezed]: `code generator` 입니다.
-- [freezed_annotation](https://pub.dev/packages/freezed_annotation): [freezed]전용 annotations을 포함하고 있는 패키지.
+- [build_runner](https://pub.dev/packages/build_runner): 코드 생성기를 실행하는 도구
+- [freezed]: 코드 생성기
+- [freezed_annotation](https://pub.dev/packages/freezed_annotation): [freezed]를 위한 어노테이션이 포함된 패키지
-### invalid_annotation_target 경고 및 생성파일의 경고를 비활성 시키기
+### invalid_annotation_target 경고 및 생성된 파일의 경고 비활성화
-[Freezed]를 `json_serializable`과 함께 사용할 계획이라면 최근 `json_serializable`와 `meta` 버전의 `invalid_annotation_target` 경고를 비활성화해야 할 수 있습니다.
+[Freezed]를 `json_serializable`과 함께 사용할 계획이라면, 최신 버전의 `json_serializable`과 `meta` 패키지 때문에 `invalid_annotation_target` 경고를 비활성화해야 할 수 있습니다.
-이를 해결하려면 프로젝트 루트에서 `analysis_options.yaml`에 아래의 내용을 추가할 수 있습니다.
+이를 위해, 프로젝트의 루트에 있는 `analysis_options.yaml` 파일에 다음을 추가할 수 있습니다:
```yaml
analyzer:
@@ -110,24 +121,17 @@ analyzer:
invalid_annotation_target: ignore
```
-## generator 실행하기
-
-코드 생성기를 실행하려면 다음 명령을 실행하십시오.
-
-```
-dart run build_runner build
-```
+## 생성기 실행
-`Flutter`프로젝트라면 아래의 명령을 수행하면 됩니다.
+코드 생성기를 실행하려면 다음 명령어를 실행하세요:
```
-flutter pub run build_runner build
+dart run build_runner watch -d
```
-대부분의 코드 생성기와 마찬가지로 [Freezed]는 `annotation`([freezed_annotation])을 모두 import해야 합니다.
-그리고 파일 상단에 `part` 키워드를 사용하세요.
+대부분의 코드 생성기와 마찬가지로, [Freezed]는 어노테이션([freezed_annotation])을 import하고 파일 상단에 `part` 키워드를 사용해야 합니다.
-이 처럼 [Freezed]를 사용하려는 파일은 아래와 같이 시작합니다.
+따라서 [Freezed]를 사용하려는 파일은 다음과 같이 시작합니다:
```dart
import 'package:freezed_annotation/freezed_annotation.dart';
@@ -136,23 +140,29 @@ part 'my_file.freezed.dart';
```
-**고려사항**
-`package:flutter/foundation.dart`도 같이 import해서 사용합니다. 그 이유는 `foundation.dart`를 가져오면 Flutter의 `devtool`에서 개체를 보기 좋게 만들기 위해 클래스도 가져오기 때문입니다 `foundation.dart`를 가져오면 [Freezed]가 자동으로 수행합니다.
+**고려사항:** `package:flutter/foundation.dart`를 import하는 것을 고려해보세요.\
+`foundation.dart`를 import하면 Flutter 개발 도구에서 객체를 보기 좋게 만들어주는 클래스들도 함께 import됩니다.\
+`foundation.dart`를 import하면 [Freezed]가 자동으로 이 작업을 수행합니다.
-## Freezed를 사용하여 모델 생성하기
+## Freezed를 사용하여 모델 만들기
-예제는 길고긴 추상적인 설명보다 이해하기 쉽습니다.
-다음은 전형적인 Freezed 클래스입니다:
+Freezed는 데이터 클래스를 만드는 두 가지 방법을 제공합니다:
+
+- [기본 생성자(Primary constructors)](#기본-생성자): 생성자를 정의하면 Freezed가 연관된 필드를 생성합니다. 이는 `factory`를 사용하여 [Primary Constructor](https://github.com/dart-lang/language/issues/2364)를 시뮬레이션하는 것입니다.
+- [일반 클래스(Classic classes)](#일반-클래스): 일반적인 Dart 클래스를 작성하면 Freezed가 `toString/==/copyWith`만 처리합니다.
+
+### 기본 생성자
+
+Freezed는 `factory` 생성자를 사용하여 기본 생성자를 구현합니다.\
+아이디어는, `factory`를 정의하면 Freezed가 나머지 모든 것을 생성하는 것입니다:
```dart
-// 이 파일은 "main.dart" 입니다.
import 'package:freezed_annotation/freezed_annotation.dart';
-import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
-// 필수: `main.dart`를 Freezed에서 생성한 코드와 연결합니다.
+// 필수: 'main.dart'와 Freezed가 생성한 코드를 연결합니다.
part 'main.freezed.dart';
-// 옵션(선택사항): Person 클래스는 직렬화 가능하므로 이 줄을 추가해야 합니다.
-// 그러나 Person이 직렬화 가능하지 않은 경우 건너뛸 수 있습니다.
+// 선택: Person 클래스는 직렬화 가능하므로 이 줄을 추가해야 합니다.
+// 하지만 Person이 직렬화 가능하지 않다면 생략할 수 있습니다.
part 'main.g.dart';
@freezed
@@ -163,39 +173,167 @@ abstract class Person with _$Person {
required int age,
}) = _Person;
- factory Person.fromJson(Map
](https://flutter.dev/docs/development/packages-and-plugins/favorites)
-[Freezed] 세계에 오신걸 환영합니다. [Freezed]는 data-classes/unions/cloning를 위한 코드 생성기입니다.
+[Freezed]에 오신 것을 환영합니다. 이 라이브러리는 데이터 클래스, 태그드 유니온(tagged unions), 중첩 클래스, 그리고 객체 복제(cloning)를 위한 또 하나의 코드 생성기입니다.
-# Freezed가 만들어진 이유
+# 3.0.0으로 마이그레이션
-Dart는 훌륭한 언어입니다. 하지만 "모델"을 정의하는 과정은 번거롭습니다.
+2.0.0에서 3.0.0으로 마이그레이션하려면 [변경 로그](https://github.com/rrousselGit/freezed/blob/master/packages/freezed/CHANGELOG.md#300---2025-02-25)와 [마이그레이션 가이드](https://github.com/rrousselGit/freezed/blob/master/packages/freezed/migration_guide.md)를 참조하세요.
-모델을 정의하려면 아래와 같은 작업이 필요합니다:
+# 동기
-생성자와 속성 정의하기
-`toString`, `operator ==`, `hashCode` 오버라이드
-객체를 복사하기 위한 `copyWith` 메서드 구현
-직렬화 및 역직렬화 처리
-게다가 Dart에는 `union types`, `pattern-matching` 같은 기능이 없습니다.
+Dart는 훌륭한 언어지만, '모델'을 정의하는 것은 지루한 작업이 될 수 있습니다. 다음과 같은 작업들이 필요합니다:
-이 모든 것을 직접 구현하려면 코드가 수백 줄로 늘어날 수도 있습니다. 이런 작업은 오류를 만들기 쉽고, 모델의 가독성을 떨어뜨릴 수 있습니다.
+- 생성자(constructor)와 프로퍼티(properties) 정의
+- `toString`, `operator ==`, `hashCode` 오버라이드
+- 객체 복제를 위한 `copyWith` 메서드 구현
+- 직렬화/역직렬화(de/serialization) 처리
-[Freezed]는 이런 부분들을 대신 처리해줌으로써 위와 같은 문제를 해결하고, 사용자가 모델 정의에 집중할 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
+이 모든 것을 구현하는 데에는 수백 줄의 코드가 필요할 수 있으며, 이는 오류가 발생하기 쉽고 모델의 가독성을 크게 해칩니다.
-| Freezed 사용 전 | Freezed 사용 후 |
-| ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
-|  |  |
+Freezed는 이 대부분의 작업을 대신 구현하여, 개발자가 모델의 정의에만 집중할 수 있도록 돕습니다.
+
+| 이전 | 이후 |
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+|  |  |
# 목차
-- [Freezed를 만들게된 이유](#Freezed를-만들게된-이유)
+- [3.0.0으로 마이그레이션](#300으로-마이그레이션)
+- [동기](#동기)
- [목차](#목차)
-- [사용방법](#사용방법)
- - [설치하기](#설치하기)
- - [invalid_annotation_target 경고 및 생성파일의 경고를 비활성 시키기](#invalid_annotation_target-경고-및-생성파일의-경고를-비활성-시키기)
- - [generator 실행하기](#generator-실행하기)
- - [Freezed를 사용하여 모델 생성하기](#Freezed를-사용하여-모델-생성하기)
- - [immutable 클래스 대신 mutable 클래스 정의하기](#Immutable-클래스-대신-Mutable-클래스-정의하기)
- - [Lists/Maps/Sets의 변경 허용하기](#listsmapssets의-변경-허용하기)
- - [copyWith의 작동방식](#copyWith의-작동방식)
- - [더 나아가기: 깊은복사](#더-나아가기-깊은복사)
- - [모델에 getters 와 메서드 추가하기](#모델에-getters와-메서드-추가하기)
- - [Asserts](#asserts)
- - [기본 값](#기본-값)
- - [데코레이터와 코멘트](#데코레이터와-코멘트)
- - [Union Types에서 Mixin 및 Interface 사용하기](#Union-Types에서-Mixin-및-Interface-사용하기)
+- [사용 방법](#사용-방법)
+ - [설치](#설치)
+ - [invalid_annotation_target 경고 및 생성된 파일의 경고 비활성화](#invalid_annotation_target-경고-및-생성된-파일의-경고-비활성화)
+ - [생성기 실행](#생성기-실행)
+ - [Freezed를 사용하여 모델 만들기](#freezed를-사용하여-모델-만들기)
+ - [기본 생성자](#기본-생성자)
+ - [모델에 getter와 메서드 추가하기](#모델에-getter와-메서드-추가하기)
+ - [Asserts](#asserts)
+ - [기본값](#기본값)
+ - [상수가 아닌 기본값](#상수가-아닌-기본값)
+ - [클래스 확장하기](#클래스-확장하기)
+ - [불변 클래스 대신 가변 클래스 정의하기](#불변-클래스-대신-가변-클래스-정의하기)
+ - [List/Map/Set의 변경 허용하기](#listmapset의-변경-허용하기)
+ - [일반 클래스](#일반-클래스)
+ - [copyWith 동작 방식](#copywith-동작-방식)
+ - [더 나아가기: 깊은 복사(Deep copy)](#더-나아가기-깊은-복사deep-copy)
+ - [데코레이터와 주석](#데코레이터와-주석)
- [FromJson/ToJson](#fromjsontojson)
- - [fromJSON - 복수의 생성자가 있는 클래스](#fromjson---복수의-생성자가-있는-클래스)
- - [제네릭 클래스 역직렬화하기](#제네릭-클래스-역직렬화하기)
- - [Union types과 Sealed classes](#Union-types과-Sealed-classes)
- - [공유속성 Shared properties](#공유속성-Shared-properties)
- - [패턴매칭(pattern-matching)을 사용하여 비공유 속성 읽기](#패턴매칭pattern-matching을-사용하여-비공유-속성읽기)
- - [권장하지 않는 패턴매칭 메소드](#)
+ - [fromJSON - 여러 생성자를 가진 클래스](#fromjson---여러-생성자를-가진-클래스)
+ - [제네릭 클래스 역직렬화](#제네릭-클래스-역직렬화)
+ - [유니온 타입](#유니온-타입)
+ - [공유 프로퍼티](#공유-프로퍼티)
+ - [패턴 매칭을 사용하여 공유되지 않는 프로퍼티 읽기](#패턴-매칭을-사용하여-공유되지-않는-프로퍼티-읽기)
+ - [유니온 타입의 개별 클래스를 위한 Mixin과 Interface](#유니온-타입의-개별-클래스를-위한-mixin과-interface)
+ - [개별 유니온 케이스 분리하기](#개별-유니온-케이스-분리하기)
+ - [(레거시) 패턴 매칭 유틸리티](#레거시-패턴-매칭-유틸리티)
- [When](#when)
- [Map](#map)
- - [환경설정](#환경설정)
- - [특정 모델의 동작변경](#특정-모델의-동작변경)
- - [전체 프로젝트의 동작변경](#전체-프로젝트의-동작변경)
-- [Utilities](#utilities)
- - [VSCode전용 Freezed extension](#VSCode전용-Freezed-extension)
- - [IntelliJ/Android Studio전용 Freezed extension](#IntelliJAndroid-Studio전용-Freezed-extension)
- - [Sponsors](#sponsors)
+ - [설정](#설정)
+ - [특정 모델의 동작 변경하기](#특정-모델의-동작-변경하기)
+ - [전체 프로젝트의 동작 변경하기](#전체-프로젝트의-동작-변경하기)
+- [유틸리티](#유틸리티)
+ - [IDE 확장 프로그램](#ide-확장-프로그램)
+ - [VSCode용 Freezed 확장 프로그램](#vscode용-freezed-확장-프로그램)
+ - [IntelliJ/Android Studio용 Freezed 확장 프로그램](#intellijandroid-studio용-freezed-확장-프로그램)
+ - [린팅(Linting)](#린팅linting)
+ - [서드파티 도구](#서드파티-도구)
+ - [DartJ](#dartj)
+ - [스폰서](#스폰서)
-# 사용방법
+# 사용 방법
-## 설치하기
+## 설치
-[Freezed]를 사용하려면 일반적으로 [build_runner]/code-generator 설정이 필요합니다.
-먼저 [build_runner]와 [Freezed]를 `pubspec.yaml` 파일에 추가합니다.
+[Freezed]를 사용하려면 일반적인 [build_runner]/코드 생성기 설정이 필요합니다.\
+먼저, `pubspec.yaml` 파일에 [build_runner]와 [Freezed]를 추가하여 설치합니다:
-만약에 `Flutter`프로젝트를 생성하는 경우에는 아래와 같이 진행합니다.
+Flutter 프로젝트의 경우:
```console
-flutter pub add freezed_annotation
-flutter pub add dev:build_runner
-flutter pub add dev:freezed
-# fromJson/toJson 생성도 사용하려면 아래를 추가하세요:
-flutter pub add json_annotation
-flutter pub add dev:json_serializable
+flutter pub add \
+ dev:build_runner \
+ freezed_annotation \
+ dev:freezed
+# freezed로 fromJson/toJson을 생성한다면 다음도 추가하세요:
+flutter pub add json_annotation dev:json_serializable
```
-만약에 `Dart`프로젝트를 생성하는 경우에는 아래와 같이 진행합니다.
+Dart 프로젝트의 경우:
```console
-dart pub add freezed_annotation
-dart pub add dev:build_runner
-dart pub add dev:freezed
-# fromJson/toJson 생성도 사용하려면 아래를 추가하세요:
-dart pub add json_annotation
-dart pub add dev:json_serializable
+dart pub add \
+ dev:build_runner \
+ freezed_annotation \
+ dev:freezed
+# freezed로 fromJson/toJson을 생성한다면 다음도 추가하세요:
+dart pub add json_annotation dev:json_serializable
```
-이렇게 하면 3개의 패키지(freezed_annotation, build_runner, freezed)가 설치됩니다.
+이 명령어는 세 개의 패키지를 설치합니다:
-- [build_runner](https://pub.dev/packages/build_runner): `code-generators`를 실행하기 위한 도구입니다.
-- [freezed]: `code generator` 입니다.
-- [freezed_annotation](https://pub.dev/packages/freezed_annotation): [freezed]전용 annotations을 포함하고 있는 패키지.
+- [build_runner](https://pub.dev/packages/build_runner): 코드 생성기를 실행하는 도구
+- [freezed]: 코드 생성기
+- [freezed_annotation](https://pub.dev/packages/freezed_annotation): [freezed]를 위한 어노테이션이 포함된 패키지
-### invalid_annotation_target 경고 및 생성파일의 경고를 비활성 시키기
+### invalid_annotation_target 경고 및 생성된 파일의 경고 비활성화
-[Freezed]를 `json_serializable`과 함께 사용할 계획이라면 최근 `json_serializable`와 `meta` 버전의 `invalid_annotation_target` 경고를 비활성화해야 할 수 있습니다.
+[Freezed]를 `json_serializable`과 함께 사용할 계획이라면, 최신 버전의 `json_serializable`과 `meta` 패키지 때문에 `invalid_annotation_target` 경고를 비활성화해야 할 수 있습니다.
-이를 해결하려면 프로젝트 루트에서 `analysis_options.yaml`에 아래의 내용을 추가할 수 있습니다.
+이를 위해, 프로젝트의 루트에 있는 `analysis_options.yaml` 파일에 다음을 추가할 수 있습니다:
```yaml
analyzer:
@@ -110,24 +121,17 @@ analyzer:
invalid_annotation_target: ignore
```
-## generator 실행하기
-
-코드 생성기를 실행하려면 다음 명령을 실행하십시오.
-
-```
-dart run build_runner build
-```
+## 생성기 실행
-`Flutter`프로젝트라면 아래의 명령을 수행하면 됩니다.
+코드 생성기를 실행하려면 다음 명령어를 실행하세요:
```
-flutter pub run build_runner build
+dart run build_runner watch -d
```
-대부분의 코드 생성기와 마찬가지로 [Freezed]는 `annotation`([freezed_annotation])을 모두 import해야 합니다.
-그리고 파일 상단에 `part` 키워드를 사용하세요.
+대부분의 코드 생성기와 마찬가지로, [Freezed]는 어노테이션([freezed_annotation])을 import하고 파일 상단에 `part` 키워드를 사용해야 합니다.
-이 처럼 [Freezed]를 사용하려는 파일은 아래와 같이 시작합니다.
+따라서 [Freezed]를 사용하려는 파일은 다음과 같이 시작합니다:
```dart
import 'package:freezed_annotation/freezed_annotation.dart';
@@ -136,23 +140,29 @@ part 'my_file.freezed.dart';
```
-**고려사항**
-`package:flutter/foundation.dart`도 같이 import해서 사용합니다. 그 이유는 `foundation.dart`를 가져오면 Flutter의 `devtool`에서 개체를 보기 좋게 만들기 위해 클래스도 가져오기 때문입니다 `foundation.dart`를 가져오면 [Freezed]가 자동으로 수행합니다.
+**고려사항:** `package:flutter/foundation.dart`를 import하는 것을 고려해보세요.\
+`foundation.dart`를 import하면 Flutter 개발 도구에서 객체를 보기 좋게 만들어주는 클래스들도 함께 import됩니다.\
+`foundation.dart`를 import하면 [Freezed]가 자동으로 이 작업을 수행합니다.
-## Freezed를 사용하여 모델 생성하기
+## Freezed를 사용하여 모델 만들기
-예제는 길고긴 추상적인 설명보다 이해하기 쉽습니다.
-다음은 전형적인 Freezed 클래스입니다:
+Freezed는 데이터 클래스를 만드는 두 가지 방법을 제공합니다:
+
+- [기본 생성자(Primary constructors)](#기본-생성자): 생성자를 정의하면 Freezed가 연관된 필드를 생성합니다. 이는 `factory`를 사용하여 [Primary Constructor](https://github.com/dart-lang/language/issues/2364)를 시뮬레이션하는 것입니다.
+- [일반 클래스(Classic classes)](#일반-클래스): 일반적인 Dart 클래스를 작성하면 Freezed가 `toString/==/copyWith`만 처리합니다.
+
+### 기본 생성자
+
+Freezed는 `factory` 생성자를 사용하여 기본 생성자를 구현합니다.\
+아이디어는, `factory`를 정의하면 Freezed가 나머지 모든 것을 생성하는 것입니다:
```dart
-// 이 파일은 "main.dart" 입니다.
import 'package:freezed_annotation/freezed_annotation.dart';
-import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
-// 필수: `main.dart`를 Freezed에서 생성한 코드와 연결합니다.
+// 필수: 'main.dart'와 Freezed가 생성한 코드를 연결합니다.
part 'main.freezed.dart';
-// 옵션(선택사항): Person 클래스는 직렬화 가능하므로 이 줄을 추가해야 합니다.
-// 그러나 Person이 직렬화 가능하지 않은 경우 건너뛸 수 있습니다.
+// 선택: Person 클래스는 직렬화 가능하므로 이 줄을 추가해야 합니다.
+// 하지만 Person이 직렬화 가능하지 않다면 생략할 수 있습니다.
part 'main.g.dart';
@freezed
@@ -163,39 +173,167 @@ abstract class Person with _$Person {
required int age,
}) = _Person;
- factory Person.fromJson(Map