- system -all users
- global -single user all repositories
- local -single user single repository
ssh -T [email protected] Test SSH connection. Check fingerprint.
ls -al ~/.ssh Checks if existing SSH keys are present.
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "[email protected]" Create SSH keys.
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)" Start ssh-agent.
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 Add SSH private key to the ssh-agent.
git config --global user.name "name"
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
git config --global core.editor "code --wait"
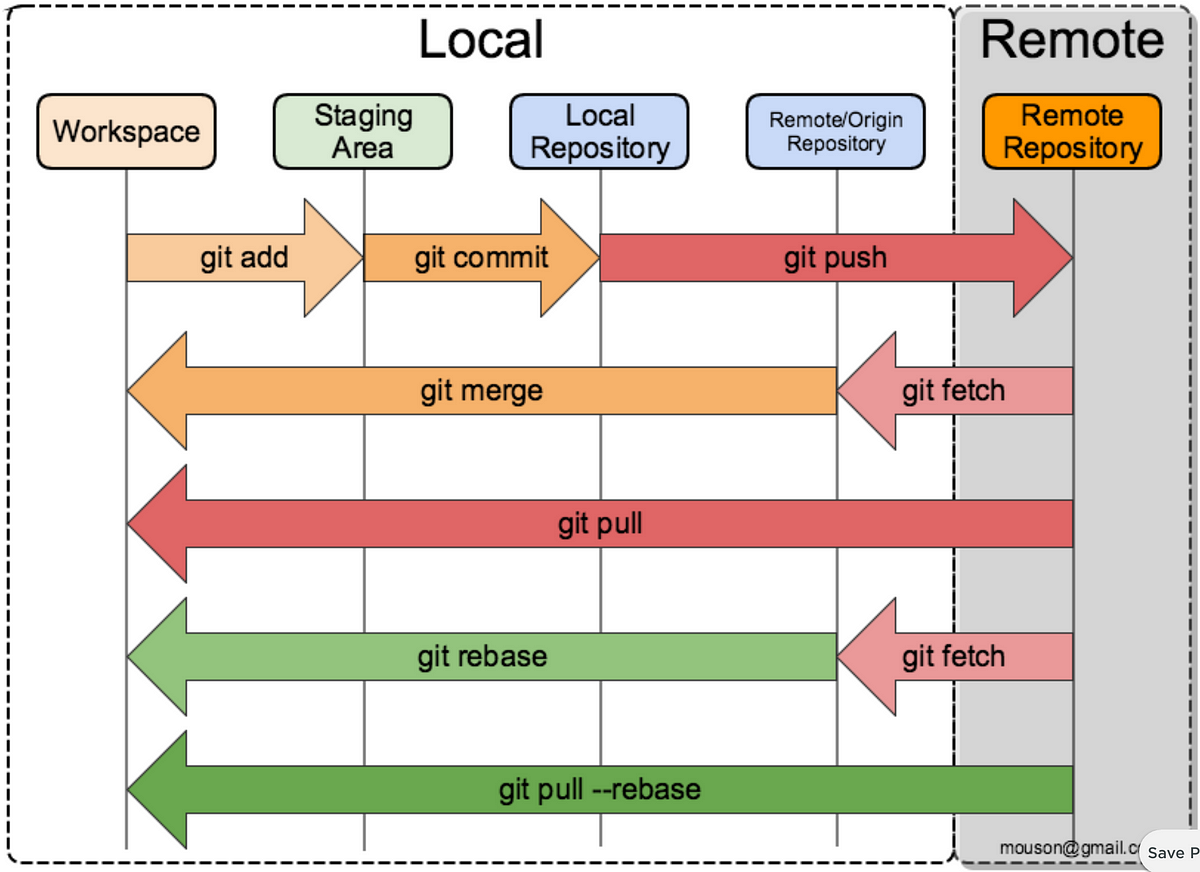
git clone <URL> Clones remote repository.
git init Creates new local repository.
git remote -v Shows short names and URLs of the remote servers.
git remote add <shortname> <url> Add remote repository.
git fetch <remote> Downloads changes from the remote repository.
git pull <remote> Same as git fetch and git merge combined.
git commit -am Stages and commits in one step.
git ls-files Shows files in staging area (index).
git status -s Short status.
git push <remote> <branch> Pushes changes to remote repository.
git mv "old name" "new name" Renames files both on the working dir and staging area.

Read the book.