This airdrop is cheaper than a whitelisted version of an airdrop, but the drawback is that the deployer needs to know all the addresses that will be able to withdraw. It is not possible to change the original list because the merkle root would change too. On the other hand a whitelisted version could be modified at any moment by an admin allowing more flexibility but paying a higher price.
npm install
npx hardhat compile
npm run testVideo explanation here Youtube Link
To try out Etherscan verification, you first need to deploy a contract to an Ethereum network that's supported by Etherscan, such as Ropsten.
In this project, copy the .env.example file to a file named .env, and then edit it to fill in the details. Enter your Etherscan API key, your Ropsten node URL (eg from Alchemy), and the private key of the account which will send the deployment transaction. With a valid .env file in place, first deploy your contract:
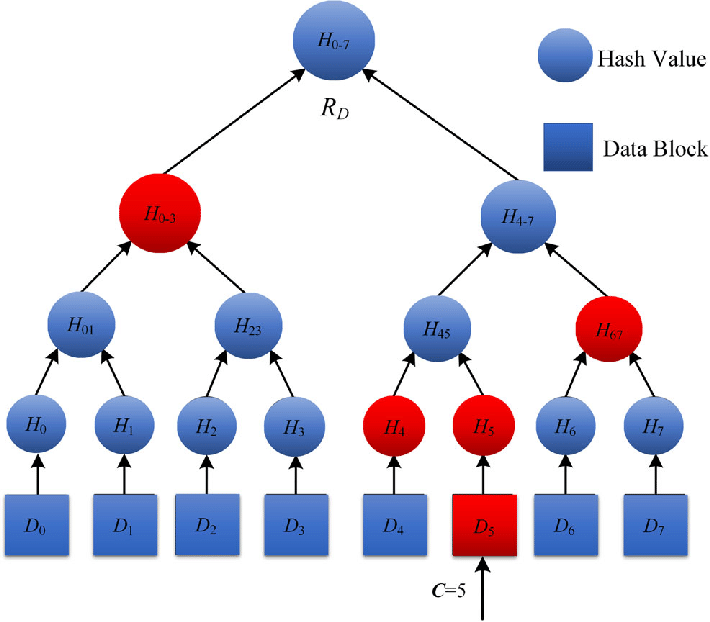
npm run verify-rinkebyThis a visual representation of how the merkle tree works, we need to have all the addresses and generate the merkle root.
Then we store the merkle root in the smart contract, this will be used as a comparison point when the users claim their tokens.
Leaves = represented at the bottom, the leaves are hashes of any information it can be the hash of an address or the hash of an address + an specific amount.
Once generated, the merkle tree doesn't completely require all the leaves it just requires what is called a merkle proof, which are the realy required hashes to get to the top, in this image they are represented in red. This merklee proof list can be generated with the same script or function used when creating the merklee tree.