This library adds TypeScript 1.7 support to Vert.x 3.2 or higher.
The library registers a new factory for verticles written in TypeScript. Just
add the library to your class path and you're done. Files with a name ending
in .ts will automatically be compiled to JavaScript when they are executed.
Type definitions
for the Vert.x JavaScript API are also provided (vertx-lang-typescript-1.1.0-typings.zip). Use them in your
favourite TypeScript editor to get auto-completion, API documentation and
meaningful error messages.
Download the library's main jar (vertx-lang-typescript-1.1.0.jar)
and put it into the lib folder of your local Vert.x installation. It will be automatically
added to the classpath by the Vert.x start script.
If your application's build is based on Maven add the following lines to your
pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>de.undercouch</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-lang-typescript</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>If you use Gradle add the following to your build.gradle:
dependencies {
compile 'de.undercouch:vertx-lang-typescript:1.1.0'
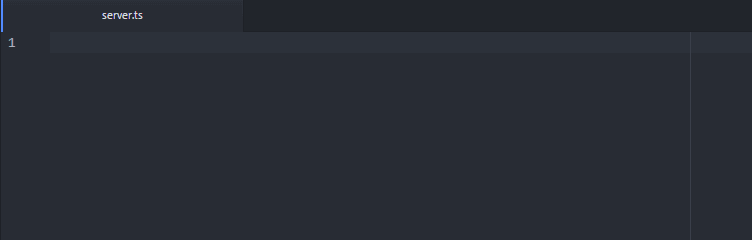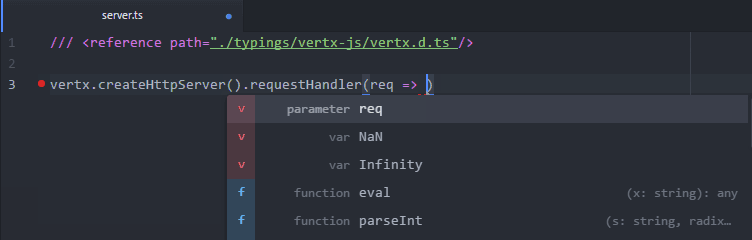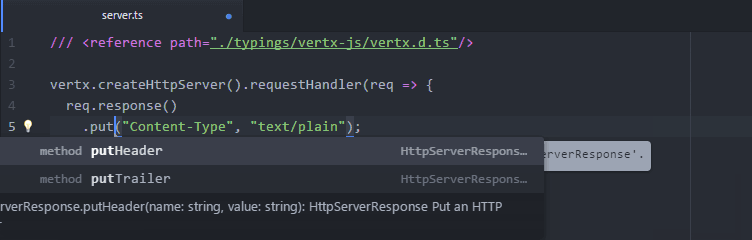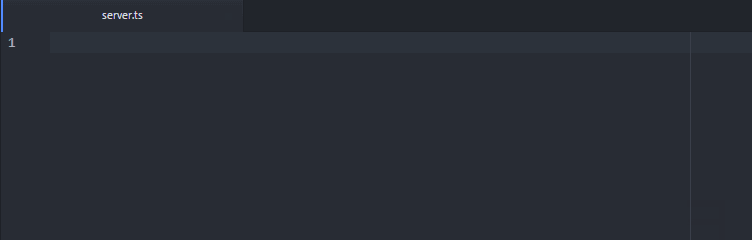
}The following script creates an HTTP server:
/// <reference path="./typings/vertx-js/vertx.d.ts" />
vertx.createHttpServer().requestHandler(req => {
req.response().putHeader("Content-Type", "text/html").end("Hello");
}).listen(8080);The TypeScript compiler runs rather slow in the JVM using the Nashorn JavaScript engine. It takes a couple of cycles before the compiler reaches its full speed. You have a number of options to improve and tweak the performance.
The fastest option is to use the V8 JavaScript engine to execute the TypeScript compiler. If J2V8 3.1.1 is available in the classpath the library automatically makes use of it.
If you execute your Vert.x application on the command line using the vertx
command then just put the right J2V8 jar for your operating system and
architecture (e.g. j2v8_linux_x86_64-3.1.1.jar for Linux or
j2v8_win32_x86_64-3.1.1.jar for Windows) into the lib folder of your local
Vert.x installation.
Otherwise follow the instructions on the J2V8 site to add the right library to your classpath.
The TypeScript compiler runs very fast in Node.js.
If the node executable is in the path the library automatically makes use of it.
If you are compiling a script multiple times in the same Vert.x container you
should set the vertx.typescriptCache system property to memory. This allows
vertx-lang-typescript to reuse already compiled scripts.
On the command line you can set this property as follows:
export VERTX_OPTS=-Dvertx.typescriptCache=memoryIn your Java program you can use
System.setProperty("vertx.typescriptCache", "memory");Caching scripts in memory only makes a difference if you, for example, deploy the same verticle multiple times. The ramp-up time, however, may still be rather long.
To mitigate this you can cache compiled scripts on disk. Set the
vertx.typescriptCache system property to disk.
export VERTX_OPTS=-Dvertx.typescriptCache=diskor
System.setProperty("vertx.typescriptCache", "disk");Cached scripts will be stored in a directory called typescript_code_cache
in the current working directory by default. You can change this location
by setting the vertx.typescriptCacheDir system property:
export VERTX_OPTS=-Dvertx.typescriptCache=disk -Dvertx.typescriptCacheDir=/tmp/typescript-cacheor
System.setProperty("vertx.typescriptCache", "disk");
System.setProperty("vertx.typescriptCacheDir", "/tmp/typescript-cache");Perform a full build with
./gradlew buildJust as Vert.x 3.x the library requires Java 8.
vertx-lang-typescript can be used from Vert.x 3.1 upwards. Go to the releases page and download the version that fits your Vert.x release.
The library is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.