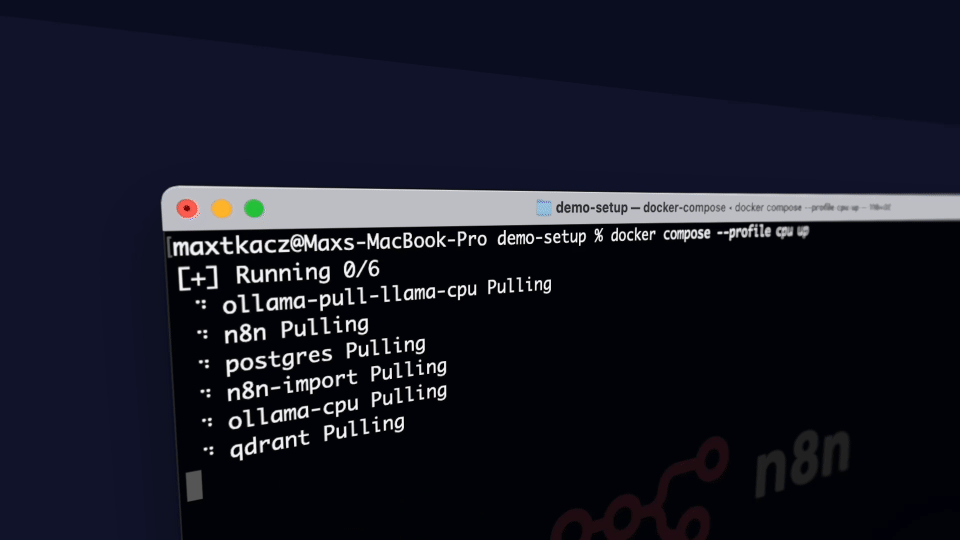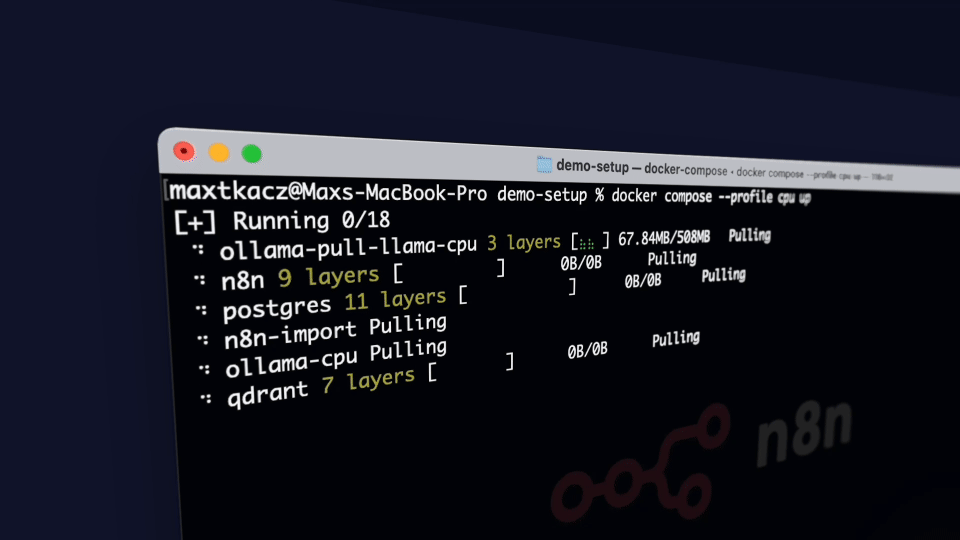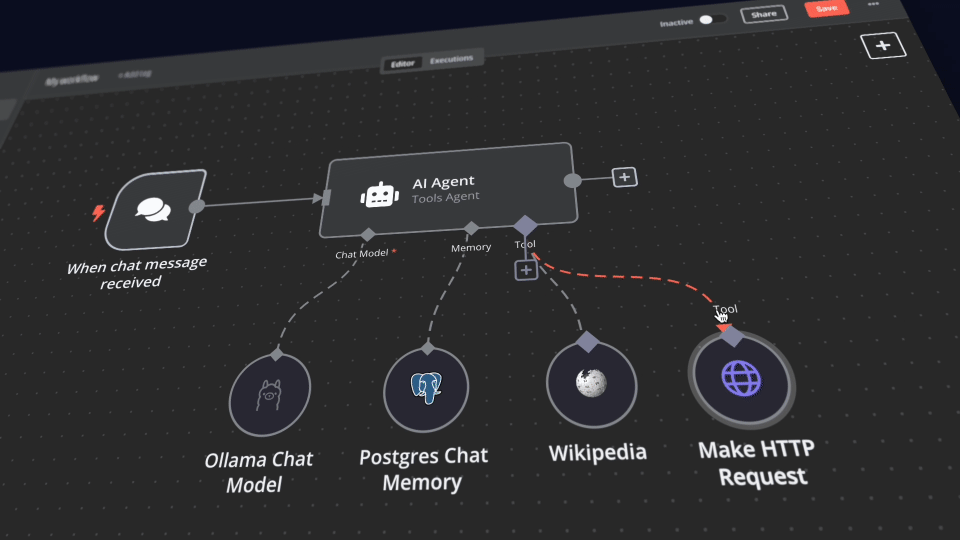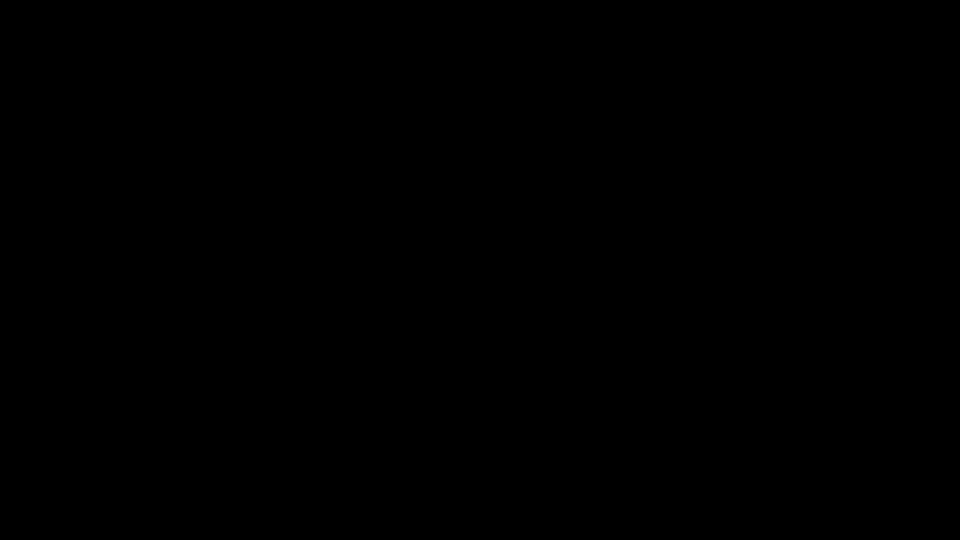
Self-hosted AI Package is an open, docker compose template that quickly bootstraps a fully featured Local AI and Low Code development environment including Ollama for your local LLMs, Open WebUI for an interface to chat with your N8N agents, and Supabase for your database, vector store, and authentication.
This is Cole's version with a couple of improvements and the addition of Supabase, Open WebUI, Flowise, SearXNG, and Caddy! Postgres was also removed since Supabase runs Postgres under the hood. Also, the local RAG AI Agent workflow from the video will be automatically in your n8n instance if you use this setup instead of the base one provided by n8n!
-
Local AI community forum over in the oTTomator Think Tank
-
GitHub Kanban board for feature implementation and bug squashing.
-
Original Local AI Starter Kit by the n8n team
-
Download my N8N + OpenWebUI integration directly on the Open WebUI site. (more instructions below)
Curated by https://github.com/n8n-io and https://github.com/coleam00, it combines the self-hosted n8n platform with a curated list of compatible AI products and components to quickly get started with building self-hosted AI workflows.
✅ Self-hosted n8n - Low-code platform with over 400 integrations and advanced AI components
✅ Supabase - Open source database as a service - most widely used database for AI agents
✅ Ollama - Cross-platform LLM platform to install and run the latest local LLMs
✅ Open WebUI - ChatGPT-like interface to privately interact with your local models and N8N agents
✅ Flowise - No/low code AI agent builder that pairs very well with n8n
✅ Qdrant - Open-source, high performance vector store with an comprehensive API. Even though you can use Supabase for RAG, this was kept unlike Postgres since it's faster than Supabase so sometimes is the better option.
✅ SearXNG - Open-source, free internet metasearch engine which aggregates results from up to 229 search services. Users are neither tracked nor profiled, hence the fit with the local AI package.
✅ Caddy - Managed HTTPS/TLS for custom domains
Before you begin, make sure you have the following software installed:
- Python - Required to run the setup script
- Git/GitHub Desktop - For easy repository management
- Docker/Docker Desktop - Required to run all services
- Clone the repository and navigate to the project directory:
git clone https://github.com/coleam00/local-ai-packaged.git
cd local-ai-packaged- Run the setup script:
python start_services.pyThat's it! The script will automatically:
- Generate secure secrets and environment variables
- Set up Supabase and all required services
- Configure Cloudflare Tunnels if you want to use them
- Start all containers with the appropriate configuration
By default, the script uses CPU mode. For other configurations, use the --profile flag:
- For Nvidia GPUs:
python start_services.py --profile gpu-nvidia - For AMD GPUs:
python start_services.py --profile gpu-amd - For Mac/Apple Silicon:
python start_services.py --profile none
Once complete, your services will be available at:
- n8n: http://localhost:5678
- Open WebUI: http://localhost:3000
- Flowise: http://localhost:3001
- SearXNG: http://localhost:8080
The setup script implements several security best practices:
- Generates cryptographically secure random values using Python's
secretsmodule - Creates proper JWT tokens for Supabase authentication
- Uses appropriate key lengths for different security requirements:
- 32 characters for standard encryption keys
- 48 characters for database passwords
- 64 characters for critical JWT secrets
- Ensures all secrets meet complexity requirements (letters, numbers, symbols)
- Avoids problematic characters that could cause service issues
- Supports secure access through Cloudflare Tunnels
- Implements automatic secret rotation and backup
- Validates all environment variables before service startup
To update all containers to their latest versions (n8n, Open WebUI, etc.), run these commands:
# Stop all services
docker compose -p localai -f docker-compose.yml -f supabase/docker/docker-compose.yml down
# Pull latest versions of all containers
docker compose -p localai -f docker-compose.yml -f supabase/docker/docker-compose.yml pull
# Start services again with your desired profile
python start_services.py --profile <your-profile>Replace <your-profile> with one of: cpu, gpu-nvidia, gpu-amd, or none.
Note: The start_services.py script itself does not update containers - it only restarts them or pulls them if you are downloading these containers for the first time. To get the latest versions, you must explicitly run the commands above.
Here are solutions to common issues you might encounter:
-
Supabase Pooler Restarting: If the supabase-pooler container keeps restarting itself, follow the instructions in this GitHub issue.
-
Supabase Analytics Startup Failure: If the supabase-analytics container fails to start after changing your Postgres password, delete the folder
supabase/docker/volumes/db/data. -
If using Docker Desktop: Go into the Docker settings and make sure "Expose daemon on tcp://localhost:2375 without TLS" is turned on
-
Supabase Service Unavailable - Make sure you don't have an "@" character in your Postgres password! If the connection to the kong container is working (the container logs say it is receiving requests from n8n) but n8n says it cannot connect, this is generally the problem from what the community has shared. Other characters might not be allowed too, the @ symbol is just the one I know for sure!
-
Windows GPU Support: If you're having trouble running Ollama with GPU support on Windows with Docker Desktop:
- Open Docker Desktop settings
- Enable WSL 2 backend
- See the Docker GPU documentation for more details
-
Linux GPU Support: If you're having trouble running Ollama with GPU support on Linux, follow the Ollama Docker instructions.
n8n is full of useful content for getting started quickly with its AI concepts and nodes. If you run into an issue, go to support.
- AI agents for developers: from theory to practice with n8n
- Tutorial: Build an AI workflow in n8n
- Langchain Concepts in n8n
- Demonstration of key differences between agents and chains
- What are vector databases?
For more AI workflow ideas, visit the official n8n AI template gallery. From each workflow, select the Use workflow button to automatically import the workflow into your local n8n instance.
- AI Agent Chat
- AI chat with any data source (using the n8n workflow too)
- Chat with OpenAI Assistant (by adding a memory)
- Use an open-source LLM (via HuggingFace)
- Chat with PDF docs using AI (quoting sources)
- AI agent that can scrape webpages
- Tax Code Assistant
- Breakdown Documents into Study Notes with MistralAI and Qdrant
- Financial Documents Assistant using Qdrant and Mistral.ai
- Recipe Recommendations with Qdrant and Mistral
The self-hosted AI starter kit will create a shared folder (by default,
located in the same directory) which is mounted to the n8n container and
allows n8n to access files on disk. This folder within the n8n container is
located at /data/shared -- this is the path you'll need to use in nodes that
interact with the local filesystem.
Nodes that interact with the local filesystem
This fork includes several enhancements to the original project:
- Simplified setup process with automatic secret generation
- Enhanced security features with environment variable validation
- Improved error handling and troubleshooting guidance
- Added support for Cloudflare Tunnels
- Streamlined container management
- Automatic backup and rotation of secrets
The following environment variables can be customized in your .env file:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD- Database password (auto-generated if not set)JWT_SECRET- JWT authentication secret (auto-generated if not set)ANON_KEY- Supabase anonymous key (auto-generated if not set)SERVICE_ROLE_KEY- Supabase service role key (auto-generated if not set)CLOUDFLARE_TUNNEL_TOKEN- Optional: Your Cloudflare Tunnel token for secure remote access
For a complete list of environment variables, see the .env.example file.
Contributions are welcome! Here's how you can help:
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch (
git checkout -b feature/amazing-feature) - Commit your changes (
git commit -m 'feat: add amazing feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin feature/amazing-feature) - Open a Pull Request
Please make sure to update tests and documentation as appropriate.
This project (originally created by the n8n team, link at the top of the README) is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see the LICENSE file for details.