Jupyter Notebook plugin for Tutor
This is a plugin for Tutor that makes it easy to integrate Jupyter notebooks in Open edX. It achieves the following:
- Install the official jupyter-xblock in the Open edX LMS and Studio.
- Run a Docker-based JupyterHub instance with a Docker spawner.
In pratice, it means that students will be allocated Docker containers with limited CPU and memory to run their custom notebooks.
tutor plugins install jupyter
Enable the plugin:
tutor plugins enable jupyter
Re-build the "openedx" Docker image to install the Jupyter XBlock:
tutor images build openedx
Launch your platform again:
tutor local launch
Print the default passport ID:
echo "$(tutor config printvalue JUPYTER_DEFAULT_PASSPORT_ID):$(tutor config printvalue JUPYTER_LTI_CLIENT_KEY):$(tutor config printvalue JUPYTER_LTI_CLIENT_SECRET)"
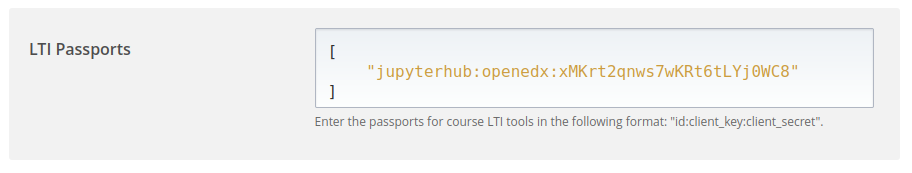
Make a note of the printed value. Go to the Studio Tools ➡️ Advanced Settings ➡️ LTI Passports. Insert the passport value:
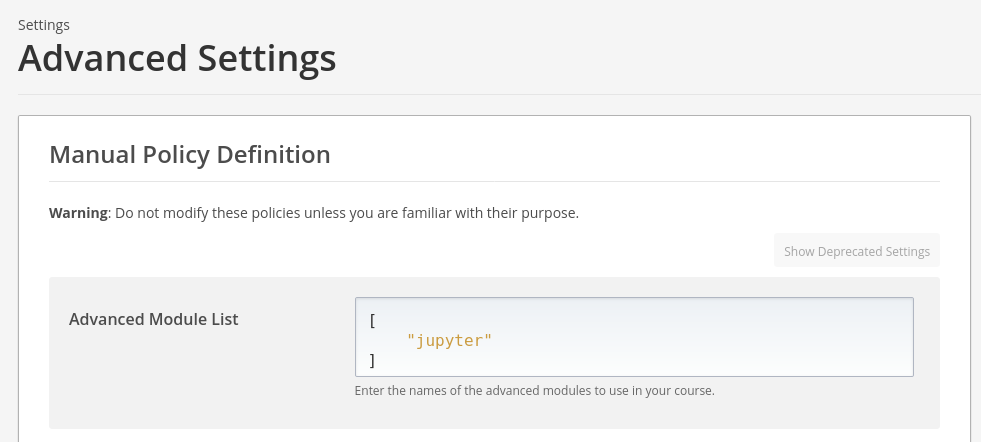
In "Advanced Module List" add "jupyter" (with quotes):
You should then be able to create an advanced Jupyter XBlock in the Studio:
> Add New Component ➡️ Advanced ➡️ Jupyter notebook
The default "hello" notebook will be pulled from the jupyter-block repository and displayed in the studio.
This plugin has the following Tutor settings. Each setting can be printed with tutor config printvalue JUPYTER_SETTING_NAME and modified with tutor config save --set JUPYTER_SETTING_NAME=value.
Default settings:
- JUPYTER_DOCKER_IMAGE_HUB (default:
"{{ DOCKER_REGISTRY }}overhangio/jupyterhub:{{ JUPYTER_VERSION }}") - JUPYTER_DOCKER_IMAGE_LAB (default:
"{{ DOCKER_REGISTRY }}overhangio/jupyterlab:{{ JUPYTER_VERSION }}") - JUPYTER_HOST (default:
"jupyter.{{ LMS_HOST }}") - JUPYTER_DEFAULT_PASSPORT_ID (default:
"jupyterhub") - JUPYTER_LTI_CLIENT_KEY (default:
"openedx") - JUPYTER_HUB_MYSQL_DATABASE (default:
"jupyterhub") - JUPYTER_HUB_MYSQL_USERNAME (default:
"jupyterhub") - JUPYTER_LAB_CPU_LIMIT (default:
None) - JUPYTER_LAB_MEMORY_LIMIT (default:
"200M")
Unique, user-specific settings:
- JUPYTER_HUB_COOKIE_SECRET (default:
"{{ 32|jupyterhub_crypt_key }}") - JUPYTER_HUB_CRYPT_KEY (default:
"{{ 32|jupyterhub_crypt_key }}") - JUPYTER_HUB_MYSQL_PASSWORD (default:
"{{ 24|random_string }}") - JUPYTER_LTI_CLIENT_SECRET (default:
"{{ 24|random_string }}")
The configuration template for the JupyterHub instance is stored in jupyterhub_config.py. This template file includes a {{ patch("jupyterhub-config") }} statement, which means that its contents can be overridden by creating an ad-hoc Tutor plugin. For instance, to add custom LTI keys to your JupyterHub instance:
from tutor import hooks
hooks.Filters.ENV_PATCHES.add_item(
(
"jupyterhub-config",
"""
# Add LTI keys to the authenticator
c.LTI11Authenticator.consumers["my-lti-key"] = "my-lti-secret"
"""
)
)
To modify the "jupyterhub" Docker image and add extra Python packages (for example), you should create a Tutor plugin that implements the "jupyterhub-dockerfile" patch:
from tutor import hooks
hooks.Filters.ENV_PATCHES.add_item(
(
"jupyterhub-dockerfile",
"""
# Install extra Python packages
RUN pip install jupyterhub-idle-culler
"""
)
)
Then build the JupyterHub image again:
tutor config save tutor images build jupyterhub
By default, Jupyter lab notebooks will be spawned that do not include extra Python packages or dependencies. To modify the "jupyterlab" Docker image and add extra Python packages (for example), you should create a Tutor plugin that implements the "jupyterlab-dockerfile" patch:
from tutor import hooks
hooks.Filters.ENV_PATCHES.add_item(
(
"jupyterlab-dockerfile",
"""
# Install extra Python packages
RUN pip install matplotlib scipy seaborn
"""
)
)
Then build the lab image again:
tutor config save tutor images build jupyterlab
You should now be able to run import matplotlib statements within your Jupyter notebooks.
This Tutor plugin is maintained by Abdul-Muqadim from Edly. Community support is available from the official Open edX forum. Do you need help with this plugin? See the troubleshooting section from the Tutor documentation.
This work is licensed under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License (AGPL).