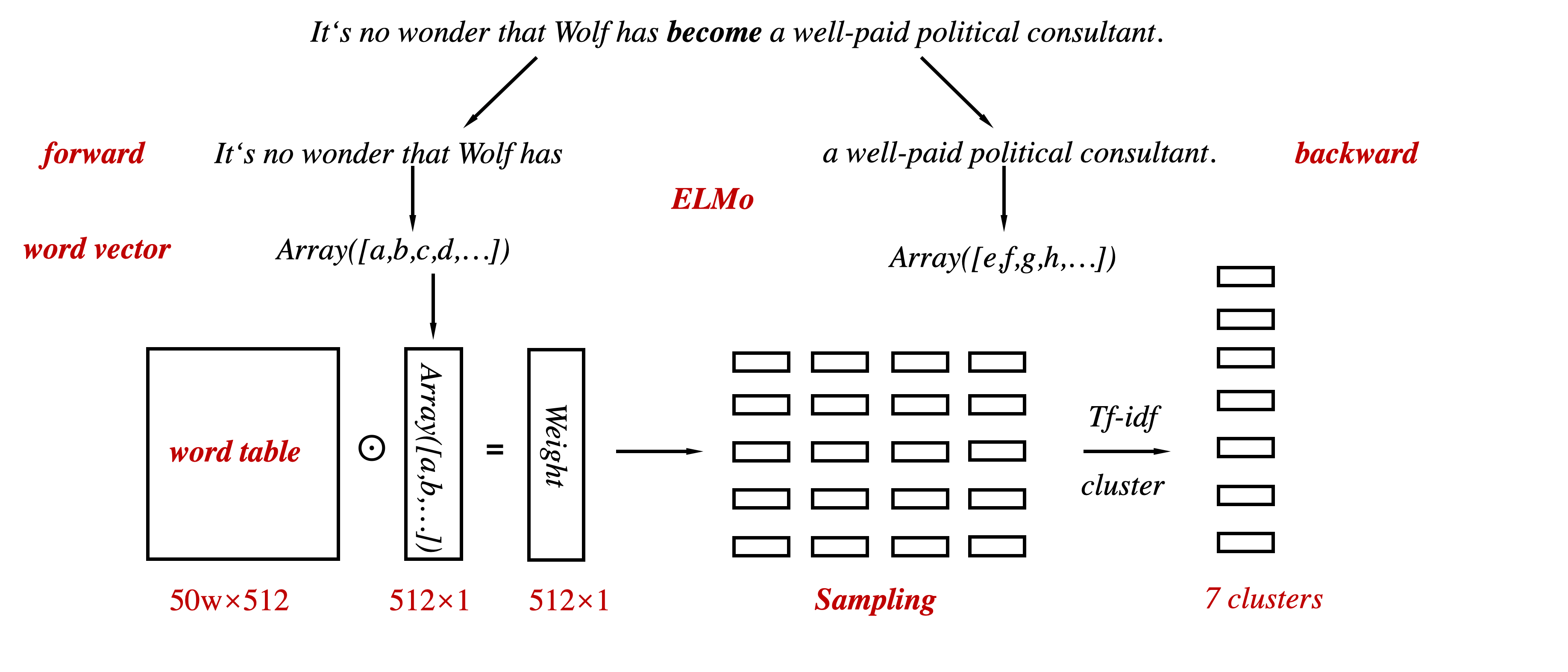
change BiLM from ELMo -> FastText, Glove;
change cluster preprocessing from tf-idf -> FastText, Glove, Bert;
in 2019.5.22
| LM | cluster | Jac. | POS | WDCG | F-NMI | F_BC | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELMo | one-hot | 19.58 | 61.45 | 33.25 | 9.28 | 58.70 | 23.34 |
| ELMo | tf-idf | 20.20 | 62.40 | 34.06 |
11.06 |
57.72 | 25.27 |
| ELMo | Bert | 19.20 | 60.23 | 30.69 | 2.65 | 54.34 | 12.00 |
| ELMo | Glove | 21.22 | 63.18 | 32.00 | 8.28 | 60.90 | 22.45 |
| ELMo | FastText | 20.14 | 62.14 | 31.47 | 7.40 | 61.39 | 21.32 |
| LM | cluster | Jac. | POS | WDCG | F-NMI | F_BC | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glove | one-hot | 19.59 | 61.66 | 32.63 | 8.66 | 59.21 | 22.64 |
| Glove | tf-idf | 19.94 | 62.50 | 33.65 | 10.69 | 57.68 | 24.83 |
| Glove | Glove | 21.31 | 63.87 |
31.83 | 8.08 | 60.88 | 22.18 |
| Glove | FastText | 19.81 | 61.78 | 30.92 | 6.49 | 61.08 | 19.91 |
| LM | cluster | Jac. | POS | WDCG | F-NMI | F_BC | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FastText | one-hot | 19.66 | 61.79 | 32.97 | 8.78 | 58.59 | 22.68 |
| FastText | tf-idf | 20.08 | 62.90 | 33.80 | 10.82 | 57.34 | 24.90 |
| FastText | Glove | 21.80 |
63.49 | 31.77 | 7.79 | 60.52 | 21.72 |
| FastText | FastText | 20.73 | 62.15 | 31.37 | 7.08 | 61.11 |
20.80 |
This repository contains reproducing code for the results in the paper:
Word Sense Induction with Neural biLM and Symmetric Patterns
The code is written in python 3.6 and runs the SemEval 2013 task 13 evaluation code provided by the SemEval 2013 workshop, which is written in Java and therefore require installed JRE.
It also requires the AllenNLP python package as well as a few other packages. Below are detailed instructions for running the code.
Prerequisites:
- Java >=1.6 installed and in PATH
- Python 3.6, preferably a clean Conda environment
Installing a clean conda environment from scratch:
# create and activate new python 3.6 conda envrionment
conda create -n spwsi python=3.6 anaconda
source activate spwsi
# for cuda support install pytorch first (see link below and note the cuda version!)
# in our system a full run w/ cuda took ~2 minutes. w/o cuda ~20 minutes
# if you don't mind that,
# you can skip next line and later run spwsi_elmo.py with arguments: --cuda -1
conda install pytorch cuda80 -c pytorch
# additional python pacakges from requirements.txt
pip install -r requirements.txt
# install spacy English model, download ELMo's output matrix and SemEval 2013 task code
python -m spacy download en
sh download_resources.shfor pytorch installation w/ cuda support see instructions at pytorch website
finally, to do the actual WSI using ELMo's LM, run spwsi_elmo.py. Arguments of spwsi_elmo.py listed below. Note that the script is creating a lemmatized vocabulary file in the resources directory and therefore needs write permission to it
we also provide spwsi_elmo_batch_run.py to run a batch of runs, such as ablation or paramters search, while keeping relevant data structures in memory.
spwsi_elmo.py script arguments:
python spwsi_elmo.py -h
usage: spwsi_elmo.py [-h] [--n-clusters N_CLUSTERS]
[--n-representatives N_REPRESENT]
[--n-samples-side N_SAMPLES_SIDE] [--cuda CUDA]
[--debug-dir DEBUG_DIR] [--disable-lemmatization]
[--disable-symmetric-patterns] [--disable-tfidf]
[--append-results-file APPEND_RESULTS_FILE]
[--run-prefix RUN_PREFIX]
[--elmo-batch-size ELMO_BATCH_SIZE]
[--prediction-cutoff PREDICTION_CUTOFF]
[--cutoff-elmo-vocab CUTOFF_ELMO_VOCAB]
BiLM Symmetric Patterns WSI Demo
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--n-clusters N_CLUSTERS
number of clusters per instance (default: 7)
--n-representatives N_REPRESENT
number of representations per sentence (default: 20)
--n-samples-side N_SAMPLES_SIDE
number of samples per representations side (default:
4)
--cuda_device CUDA_DEVICE
cuda device for ELMo (-1 to disable) (default: 0)
--debug-dir DEBUG_DIR
logs and keys are written will be written to this dir
(default: debug)
--disable-lemmatization
disable ELMO prediction lemmatization (default: False)
--disable-symmetric-patterns
disable "x and y" symmetric pattern and predict
substitutes inplace (default: False)
--disable-tfidf disable tfidf transformer (default: False)
--run-postfix RUN_POSTFIX
will be appended to log file names and products
(default: )
--lm-batch-size LM_BATCH_SIZE
ELMo prediction batch size (optimization only)
(default: 50)
--prediction-cutoff PREDICTION_CUTOFF
ELMo predicted distribution top K cutoff (default: 50)
--cutoff-lm-vocab CUTOFF_LM_VOCAB
optimization: only use top K words for faster output
matrix multiplication (default: 50000)The default parameters specified above are used in the paper
to run on cuda device 1
python spwsi_elmo.py --cuda_device 1After running spwsi_elmo.py, a detailed execution log will be available inside "debug" directory after running the script.
Additionally, a SemEval .key file will be created inside the "debug" dir. This file will contain a mapping from the task dataset entries to their induced senses. The SemEval task code evaluates this mapping and produce two metric scores: FNMI and FBC as described in the paper. You can re-run this key file evaluation using evaluate_key.sh
Developed and tested on Ubuntu 16, Cuda 8.0
-
download_resources.sh - download SemEval 2013 task dataset and ELMo's output matrix weights and put them in the resource directory
-
spwsi_elmo.py - induce senses from SemEval 2013 task dataset
-
spwsi_elmo_ablation_batch.py - run a batch of induction runs efficiently, provided scenarios: ablation, search, n_clusters. edit code and run for modifications
-
evaluate_key.sh - after each run, a SemEval .key file is produced in the debug dir, you can re-run and print task scoring on the .key file produced using this script
-
spwsi/bilm_interface.py - if you want to use a custom biLM, this interface should be implemented
As detailed in the paper, the proposed method achieves these scores on SemEval 2013 task 13: Score: mean(standard deviation) FNMI: 11.26(0.43) FBC: 57.49(0.23) AVG: 25.43(0.48)