Snapex7 is an Elixir wrapper for the Snap7 library. Snap7 i san open source, 32/64 bit, multi-platform Ethernet communication suite for interfacing natively with Siemens S7 PLCs.
-
Snapex7 is developer for snap7 1.4.2 and Elixir 1.8.1. It is tested on:
- Ubuntu
- MacOS
- Nerves
-
Note Currently only the Client implementation as synchronous of Snap7 is available. Future implementations can be found in our TODO section.
- Installation
- Target Compatibility
- Using Snapex7
- Further Documentation and Examples
- Contributing to this Repo
- TODO
The package can be installed by adding snapex7 to your list of dependencies in mix.exs:
def deps do
[
{:snapex7, "~> 0.1.2"}
]
endFetch the dependency by running mix deps.get in your terminal.
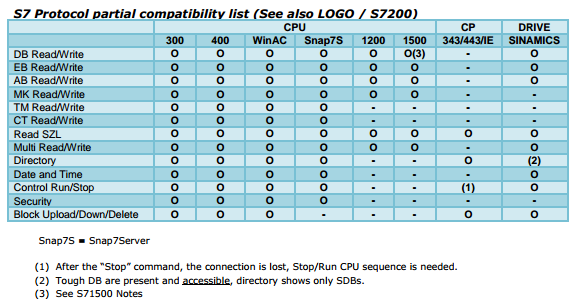
Many hardware components equipped with an Ethernet port can communicate via the S7 protocol. Check compatibility with the component that you are using:
- Snap7 full compatibility documentation can be found at pg.33 Snap7-refman.pdf
Here is a summary compatibility table from the documentation above:
Start a Snapex7.Client and connect it to the PLC's IP, where:
- port: C port process
- controlling_process: where events get sent
- queued_messages: queued messages when in passive mode (WIP).
- ip: the address of the server
- rack: the rack of the server.
- slot: the slot of the server.
- is_active: active or passive mode (WIP).
iex> {:ok, pid} = Snapex7.Client.start_link()
iex> Snapex7.Client.connect_to(pid, ip: "192.168.0.1", rack: 0, slot: 1)- Connect to a S7 server.
The following options are available:
:active- (trueorfalse) specifies whether data is received as messages or by calling "Data I/O functions".:ip- (string) PLC/Equipment IPV4 Address (e.g., "192.168.0.1"):rack- (int) PLC Rack number (0..7).:slot- (int) PLC Slot number (1..31).
iex> :ok = Snapex7.Client.connect_to(pid, ip: "192.168.0.1", rack: 0, slot: 1)- Disconnects gracefully the Client from the PLC.
iex> :ok = Snapex7.Client.disconnect(pid)- Get connected returns the connection status.
iex> {:ok, boolean} = Snapex7.Client.get_connected(pid)- Reads a data area from a PLC.
The following options are available:
:area- (atom) Area Identifier. See @area_types.:db_number- (int) DataBase number, ifarea: :DBotherwise is ignored.:start- (int) An offset to start.:amount- (int) Amount of words to read/write.:word_len- (atom) Word size See @word_types.
iex> {:ok, resp_binary} =
Snapex7.Client.read_area(pid,
area: :DB,
word_len: :byte,
start: 2,
amount: 4,
db_number: 1
)- Write a data area from a PLC..
The same options of
Snapex.Client.read_areaare available here plus::data- (atom) buffer to write.
iex> :ok =
Snapex7.Client.write_area(pid,
area: :DB,
word_len: :byte,
start: 2,
amount: 4,
db_number: 1,
data: <<0x42, 0xCB, 0x00, 0x00>>
)-
Lean functions of
Snapex.Client.read_areaandSnapex.Client.write_areafor different types of ... are implemented:db_read&db_write: for PLC Database.ab_read&ab_write: for PLC process outputs.eb_read&eb_write: for PLC process inputs.mb_read&mb_write: for PLC merkers.tm_read&tm_write: for PLC timers.ct_read&ct_write: for PLC counters.
-
Write and Read different kinds of variables from a PLC in a single call. It can do so with it can read DB, inputs, outputs, Merkers, Timers and Counters.
iex> data1 = %{
area: :DB,
word_len: :byte,
db_number: 1,
start: 2,
amount: 4,
data: <<0x42, 0xCB, 0x20, 0x10>>
}
iex> data2 = %{
area: :PA,
word_len: :byte,
db_number: 1,
start: 0,
amount: 1,
data: <<0x0F>>
}
iex> r_data1 = %{
area: :DB,
word_len: :byte,
db_number: 1,
start: 2,
amount: 4
}
iex> r_data2 = %{
area: :PA,
word_len: :byte,
db_number: 1,
start: 0,
amount: 1
}
iex> :ok = Snapex7.Client.write_multi_vars(pid, data: [data1, data2])
iex> {:ok, [binary]} = Snapex7.Client.read_multi_vars(pid, data: [r_data1, r_data2])When a response returns an error, it will have the following format:
iex> {:error, %{eiso: nil, es7: nil, etcp: 113}}- eiso: returns an atom with the ISO TCP error.
- es7: returns an atom with the S7 protocol error.
- etcp: returns an int TCP error or nil (Depends on your OS). Example: see TCP_error_info for Ubuntu OS.
See Snap7-refman.pdf pg.252 for further error info.
Arguments definition for each particular memory block:
@block_types [
OB: 0x38, # Organization block
DB: 0x41, # Data block
SDB: 0x42, # System data block
FC: 0x43, # Function
SFC: 0x44, # System function
FB: 0x45, # Functional block
SFB: 0x46 # System functional block
]
@connection_types [
PG: 0x01, # Programming console
OP: 0x02, # Siemens HMI panel
S7_basic: 0x03 # Generic data transfer connection
]
@area_types [
PE: 0x81, # Process Inputs
PA: 0x82, # Process Outputs
MK: 0x83, # Merkers
DB: 0x84, # DB
CT: 0x1C, # Counters
TM: 0x1D # Timers
]
@word_types [
bit: 0x01,
byte: 0x02,
word: 0x04,
d_word: 0x06,
real: 0x08,
counter: 0x1C,
timer: 0x1D
]Snapex7 has further client functions implementation which can be found at Snapex7 Hexdocs.
-
Client function types in Hexdocs:
- Administrative
- Data IO
- Directory
- Block oriented
- Date/Time
- System Info
- PLC Control
- Security
- Low level
- Miscellaneous
-
Additional examples of usage can be found in the testing section of the project /test/s7_client_text/
- Note: Tests where writen with a local preconfigured PLC.
-
Snap7 source code and documentation can be found at Snap7-refman.pdf
- Fork our repository on github.
- Fix or add what is needed.
- Commit to your repository
- Issue a github pullrequest.
If you wish to clone this Repo use:
git clone --recursive [email protected]:valiot/snap7.git
See LICENSE.
- Better handling c code
- Server implementation
- Partner implementation
- Asynchronous Client implementation