Sans-I/O WebRTC implementation in Rust
RTC is a pure Rust implementation of WebRTC using a sans-I/O architecture. Unlike traditional WebRTC libraries, RTC separates protocol logic from I/O operations, giving you complete control over networking, threading, and async runtime integration.
Sans-I/O (without I/O) is a design pattern where the library handles protocol logic but you control all I/O operations. Instead of the library performing network reads and writes directly, you feed it network data and it tells you what to send.
Benefits:
- 🚀 Runtime Independent - Works with tokio, async-std, smol, or blocking I/O
- 🎯 Full Control - You control threading, scheduling, and I/O multiplexing
- 🧪 Testable - Protocol logic can be tested without real network I/O
- 🔌 Flexible - Easy integration with existing networking code
The sans-I/O architecture uses a simple event loop with six core methods:
poll_write()- Get outgoing network packets to send via UDPpoll_event()- Process connection state changes and notificationspoll_read()- Get incoming application messages (RTP, RTCP, data)poll_timeout()- Get next timer deadline for retransmissions/keepaliveshandle_read()- Feed incoming network packets into the connectionhandle_timeout()- Notify about timer expiration
Additional methods for external control:
- handle_write() - Queue application messages (RTP/RTCP/data) for sending
- handle_event() - Inject external events into the connection
use rtc::peer_connection::RTCPeerConnection;
use rtc::peer_connection::configuration::RTCConfigurationBuilder;
use rtc::peer_connection::event::{RTCPeerConnectionEvent, RTCTrackEvent};
use rtc::peer_connection::state::RTCPeerConnectionState;
use rtc::peer_connection::message::RTCMessage;
use rtc::peer_connection::sdp::RTCSessionDescription;
use rtc::shared::{TaggedBytesMut, TransportContext, TransportProtocol};
use rtc::sansio::Protocol;
use std::time::{Duration, Instant};
use tokio::net::UdpSocket;
use bytes::BytesMut;
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// Setup peer connection
let config = RTCConfigurationBuilder::new().build();
let mut pc = RTCPeerConnection::new(config)?;
// Signaling: Create offer and set local description
let offer = pc.create_offer(None)?;
pc.set_local_description(offer.clone())?;
// TODO: Send offer.sdp to remote peer via your signaling channel
// signaling_channel.send_offer(&offer.sdp).await?;
// TODO: Receive answer from remote peer via your signaling channel
// let answer_sdp = signaling_channel.receive_answer().await?;
// let answer = RTCSessionDescription::answer(answer_sdp)?;
// pc.set_remote_description(answer)?;
// Bind UDP socket
let socket = UdpSocket::bind("0.0.0.0:0").await?;
let local_addr = socket.local_addr()?;
let mut buf = vec![0u8; 2000];
'EventLoop: loop {
// 1. Send outgoing packets
while let Some(msg) = pc.poll_write() {
socket.send_to(&msg.message, msg.transport.peer_addr).await?;
}
// 2. Handle events
while let Some(event) = pc.poll_event() {
match event {
RTCPeerConnectionEvent::OnConnectionStateChangeEvent(state) => {
println!("Connection state: {state}");
if state == RTCPeerConnectionState::Failed {
return Ok(());
}
}
RTCPeerConnectionEvent::OnTrack(RTCTrackEvent::OnOpen(init)) => {
println!("New track: {}", init.track_id);
}
_ => {}
}
}
// 3. Handle incoming messages
while let Some(message) = pc.poll_read() {
match message {
RTCMessage::RtpPacket(track_id, packet) => {
println!("RTP packet on track {track_id}");
}
RTCMessage::DataChannelMessage(channel_id, msg) => {
println!("Data channel message");
}
_ => {}
}
}
// 4. Handle timeouts
let timeout = pc.poll_timeout()
.unwrap_or(Instant::now() + Duration::from_secs(86400));
let delay = timeout.saturating_duration_since(Instant::now());
if delay.is_zero() {
pc.handle_timeout(Instant::now())?;
continue;
}
// 5. Multiplex I/O
tokio::select! {
_ = stop_rx.recv() => {
break 'EventLoop,
}
_ = tokio::time::sleep(delay) => {
pc.handle_timeout(Instant::now())?;
}
Ok(message) = message_rx.recv() => {
pc.handle_write(message)?;
}
Ok(event) = event_rx.recv() => {
pc.handle_event(event)?;
}
Ok((n, peer_addr)) = socket.recv_from(&mut buf) => {
pc.handle_read(TaggedBytesMut {
now: Instant::now(),
transport: TransportContext {
local_addr,
peer_addr,
ecn: None,
transport_protocol: TransportProtocol::UDP,
},
message: BytesMut::from(&buf[..n]),
})?;
}
}
}
pc.close()?;
Ok(())
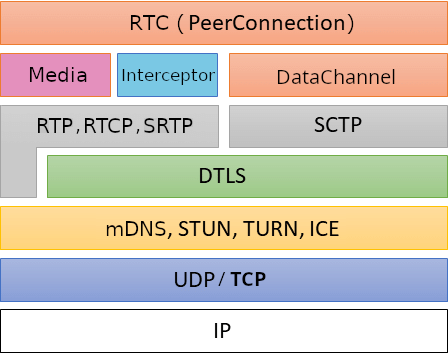
}- ✅ ICE (Interactive Connectivity Establishment) - NAT traversal with STUN/TURN
- ✅ DTLS (Datagram Transport Layer Security) - Encryption for media and data
- ✅ SCTP (Stream Control Transmission Protocol) - Reliable data channels
- ✅ RTP/RTCP - Real-time media transport and control
- ✅ SDP (Session Description Protocol) - Offer/answer negotiation
- ✅ Data Channels - Bidirectional peer-to-peer data transfer
- ✅ Media Tracks - Audio/video transmission
- ✅ Trickle ICE - Progressive candidate gathering
- ✅ Simulcast & SVC - Scalable video coding
The repository includes comprehensive examples demonstrating various use cases:
- data-channels-offer-answer - Complete data channel setup with signaling
- reflect - Echo server that reflects media back to sender
- save-to-disk-vpx - Receive and save VP8/VP9 video
- play-from-disk-vpx - Send VP8/VP9 video from disk
Run an example:
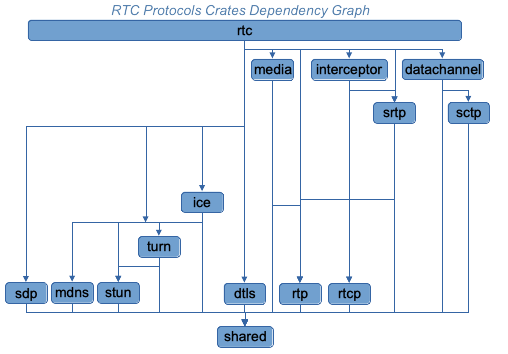
cargo run --example data-channels-offer --features examplesRTC is built from composable crates, each implementing a specific protocol:
 RTC
RTC
 Media
Media
 Interceptor
Interceptor
 DataChannel
DataChannel
 RTP
RTP
 RTCP
RTCP
 SRTP
SRTP
 SCTP
SCTP
 DTLS
DTLS
 STUN
STUN
 TURN
TURN
 ICE
ICE
 SDP
SDP
 Shared
Shared
use rtc::data_channel::RTCDataChannelInit;
fn example(mut pc: RTCPeerConnection) -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// Create a data channel
let init = RTCDataChannelInit {
ordered: true,
max_retransmits: None,
..Default::default()
};
let mut dc = pc.create_data_channel("my-channel", Some(init))?;
// Send data
dc.send_text("Hello, WebRTC!")?;
Ok(())
}use rtc::media_stream::MediaStreamTrack;
use rtc::rtp_transceiver::rtp_sender::{RTCRtpCodec, RtpCodecKind};
fn example(mut pc: RTCPeerConnection) -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// Create a video track
let track = MediaStreamTrack::new(
"stream-id".to_string(),
"track-id".to_string(),
"Camera".to_string(),
RtpCodecKind::Video,
None,
12345, // SSRC
RTCRtpCodec::default(),
);
// Add to peer connection
let sender_id = pc.add_track(track)?;
Ok(())
}WebRTC requires an external signaling channel (e.g., WebSocket, HTTP) to exchange offers and answers:
fn example(mut pc: RTCPeerConnection) -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// Create and send offer
let offer = pc.create_offer(None)?;
pc.set_local_description(offer.clone())?;
// Send offer.sdp via your signaling channel
// Receive and apply answer
// let answer = receive_answer_from_signaling()?;
// pc.set_remote_description(answer)?;
Ok(())
}This implementation follows these specifications:
- W3C WebRTC 1.0 - Main WebRTC API specification
- RFC 8829 - JSEP: JavaScript Session Establishment Protocol
- RFC 8866 - SDP: Session Description Protocol
- RFC 8445 - ICE: Interactive Connectivity Establishment
- RFC 6347 - DTLS: Datagram Transport Layer Security
- RFC 8831 - WebRTC Data Channels
- RFC 3550 - RTP: Real-time Transport Protocol
- API Documentation - Complete API reference
- Examples - Working code examples
- Sans-I/O Pattern - Detailed explanation of the sans-I/O design
- WebRTC for the Curious - Comprehensive WebRTC guide
# Build the library
cargo build
# Run tests
cargo test
# Build documentation
cargo doc --open
# Run examples
cargo run --example data-channels-offer --features examplesContributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.
This project is licensed under either of:
- MIT License (LICENSE-MIT or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
- Apache License, Version 2.0 (LICENSE-APACHE or http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
at your option.
Special thanks to all contributors and the WebRTC-rs community for making this project possible.