-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Blockchain
Blockchain is an emerging technology that can radically improve banking, supply chain, and other transaction networks and can create new opportunities for innovation. Businesses contain many examples of networks of individuals and organizations that collaborate to create value and wealth. These networks work together in markets that exchange assets in the form of goods and services between the participants.
Blockchain technology provides the basis for a dynamic shared ledger that can be applied to save time when recording transactions between parties, remove costs associated with intermediaries, and reduce risks of fraud and tampering.
Annual Hash Growth: Growth in the total network computations over the past 365 days
Block Height: The total number of blocks in the blockchain
Block Interval: Average amount of time between blocks
Block Size: The storage size of each block (i.e. megabytes)
BlockChain Size: The storage size of the blockchain (i.e. gigabytes)
Daily Blocks: Number of blocks found each day
Chain Value Density: The value of bitcoin's blockchain, in terms of dollars per megabyte
Daily Transactions: The number of transactions included in the blockchain per day
Difficulty: The minimum proof-of-work threshold required for a bitcoin miner to mine a block
Fee Percentage: Average fee paid as a percentage of transaction volume
Fee Rate: Average fee paid per transaction
Two-Week Hash Growth: Growth in the total network computations over the past 14 days
Hash Rate: The number of block solutions computed per second by all miners
Market Capitalization: The market value of all bitcoin in circulation
Metcalfe's Law - TX: A variant of Metcalfe's Law in which price is divided by n log n number of daily transactions
Metcalfe's Law - UTXO: A variant of Metcalfe's Law in which price is divided by n log n number of unspent transaction outputs
Miner Revenue Value: The amount of dollars earned by the mining network
Miner Revenue: The amount of bitcoin earned by the mining network, in the form of block rewards and transaction fees
Money Supply: The amount of bitcoin in circulation
Output Value: The dollar value of all outputs sent over the network
Output Volume: The amount of Bitcoin sent over the network
Bitcoin Price: The amount of dollars a single bitcoin is worth
Quarterly Hash Growth: Growth in the total network computations in the past 90 days
Total Transactions: The running total number of transactions processed by the Bitcoin network
Transaction Amount: The average amount of bitcoin moved per transaction
Fees Value: The dollar value of mining fees
Transaction Fees: The amount of bitcoin paid to miners in fees
Transaction Size: The average data size of a transaction
Transaction Value: The average dollar value moved in each transaction
Transactions per Block: The number of transactions in each block
Average UTXO Amount: The average amount of bitcoin contained in each unspent transaction output
UTXO Growth: The net number of unspent transaction outputs created
UTXO Set Size: The total number of unspent transaction outputs
Average UTXO Value: The average dollar value of each uspent transaction output
Velocity - Daily: The proportion of the money supply transacted each day
Velocity - Quarterly: The proportion of the money supply transacted each day, computed on a rolling-quarter basis
Velocity of Money: How many times the money supply changes hands in a given year
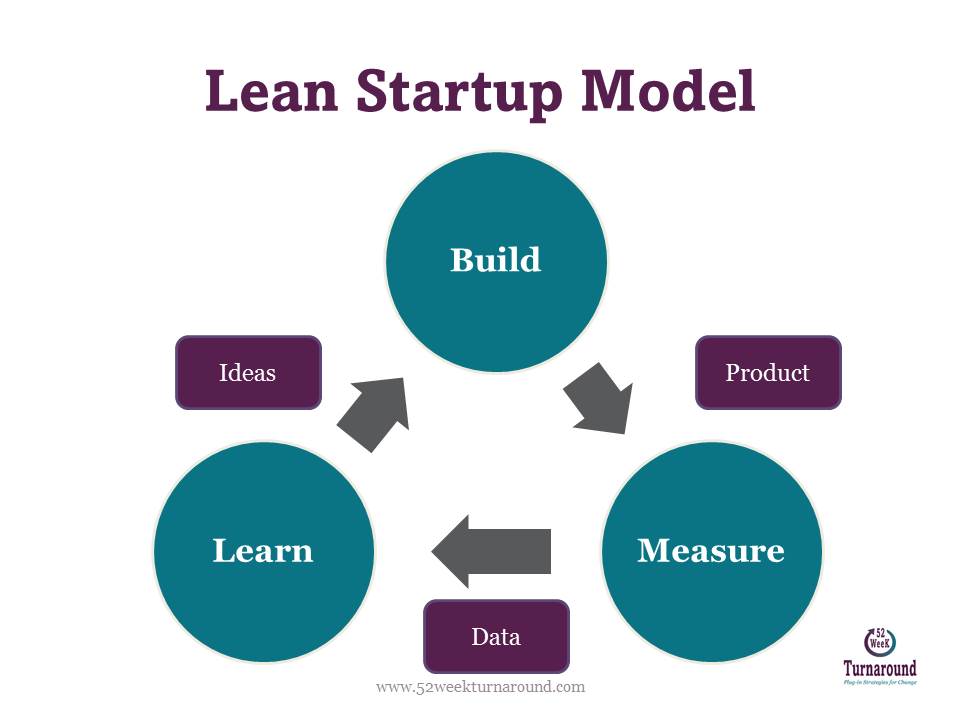
Agile, MVP, Lean Startup
微处理架构——处理复杂事物
许多公司,比如Amazon、eBay和NetFlix,通过采用微处理结构模式解决了上述问题。其思路不是开发一个巨大的单体式的应用,而是将应用分解为小的、互相连接的微服务。
一个微服务一般完成某个特定的功能,比如游戏玩家账号管理、游戏道具管理等等。每一个微服务都是微型六角形应用,都有自己的业务逻辑和适配器。一些微服务还会发布API给其它微服务和应用客户端使用。其它微服务完成一个Web UI,运行时,每一个实例可能是一个云VM或者是Docker容器。